My article “SQL vs NoSQL: The Variations” famous that the road between SQL and NoSQL databases has turn into more and more blurred, with every camp adopting options from the opposite. MySQL 5.7+ InnoDB databases and PostgreSQL 9.2+ each instantly assist JSON doc sorts in a single area. This text will look at the MySQL 9.1 JSON implementation in additional element.
Be aware that any database will settle for JSON paperwork as a single-string blob. Nevertheless, MySQL and PostgreSQL assist validated JSON information in actual key/worth pairs relatively than a primary string.
Key Takeaways
- JSON doc sorts are instantly supported in MySQL 5.7+ InnoDB databases and PostgreSQL 9.2+, however they need to be used properly on account of limitations in direct indexing.
- JSON is finest fitted to sparsely populated information, customized attributes, hierarchical buildings, and instances requiring flexibility. It mustn’t change normalized columns for regularly queried or listed information.
- MySQL gives a wide range of features to create, validate, search, and modify JSON objects. These embrace
JSON_ARRAY(),JSON_OBJECT(),JSON_QUOTE(), JSON_TYPE(), JSON_VALID(), JSON_CONTAINS(), JSON_SEARCH(),andfeatures like JSON_SET() and JSON_MERGE_PATCH()for updating JSON paperwork utilizing path notation. - MySQL 9.1 helps purposeful indexing on generated columns derived from JSON information, enabling environment friendly querying of particular JSON components.
- Whereas MySQL helps JSON, it stays a relational database. Excessively utilizing JSON might negate SQL’s advantages.
Simply As a result of You Can Retailer JSON Paperwork in MySQL JSON Columns…
… it doesn’t imply you need to.
Normalization is a method used to optimize the database construction. The First Regular Type (1NF) rule governs that each column ought to maintain a single worth — which is clearly damaged by storing multi-value JSON paperwork.
In case you have clear relational information necessities, use applicable single-value fields. JSON must be used sparingly as a final resort. JSON worth fields can’t be listed instantly, so keep away from utilizing them on columns which are up to date or searched recurrently.
Practical indexing on generated columns derived from JSON lets you index components of your JSON object, bettering question efficiency.
That stated, there are good JSON use instances for sparsely populated information or customized attributes.
Create a Desk With a JSON Information Sort Column
Think about a store promoting books. All books have an ID, ISBN, title, writer, variety of pages, and different clear relational information.
Now, if you wish to add any variety of class tags to every ebook. You could possibly obtain this in SQL utilizing:
- A tag desk that saved every tag identify with a singular ID and
- A tagmap desk with many-to-many information mapping ebook IDs to tag IDs
It’ll work, however it’s cumbersome and appreciable effort for a minor characteristic. Due to this fact, you may outline a MySQL JSON area for tags in your MySQL database’s ebook desk:
CREATE TABLE `ebook` (
`id` MEDIUMINT() UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`title` VARCHAR(200) NOT NULL,
`tags` JSON DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=INNODB;
MySQL JSON columns can’t have a default worth, can’t be used as a major key, can’t be used as a overseas key, or have direct indexes.
However, with MySQL 9.1, you may create purposeful indexes on generated columns derived from JSON information, which allows indexing particular components inside a JSON doc. These generated columns may be digital or saved and listed as secondary indexes.
ALTER TABLE ebook
ADD COLUMN first_tag VARCHAR(50) AS (JSON_UNQUOTE(tags->'$[0]')),
ADD INDEX idx_first_tag (first_tag);Including JSON Information
Entire JSON paperwork may be handed in INSERT or UPDATE statements, making it simple to maneuver JSON to MySQL for storage and manipulation.
For instance, our ebook tags may be handed as an array (inside a string):
INSERT INTO `ebook` (`title`, `tags`)
VALUES (
'ECMAScript 2015: A SitePoint Anthology',
'["JavaScript", "ES2015", "JSON"]'
);
JSON may also be created with these:
- JSON_ARRAY() perform, which creates arrays. For instance:
-- returns [1, 2, "abc"]: SELECT JSON_ARRAY(1, 2, 'abc'); - JSON_OBJECT() perform, which creates objects. For instance:
-- returns {"a": 1, "b": 2}: SELECT JSON_OBJECT('a', 1, 'b', 2); - JSON_QUOTE() perform, which quotes a string as a JSON worth. For instance:
-- returns "[1, 2, "abc"]": SELECT JSON_QUOTE('[1, 2, "abc"]'); - CAST(anyValue AS JSON) perform, which casts a worth as a JSON kind for validity:
SELECT CAST('{"a": 1, "b": 2}' AS JSON);
The JSON_TYPE() perform lets you examine JSON worth sorts. It ought to return OBJECT, ARRAY, a scalar kind (INTEGER, BOOLEAN, and many others), NULL, or an error. For instance:
SELECT JSON_TYPE('[1, 2, "abc"]');
SELECT JSON_TYPE('{"a": 1, "b": 2}');
SELECT JSON_TYPE('{"a": 1, "b": 2');
The JSON_VALID() perform returns 1 if the JSON is legitimate or 0 in any other case:
SELECT JSON_TYPE('[1, 2, "abc"]');
SELECT JSON_TYPE('{"a": 1, "b": 2}');
SELECT JSON_TYPE('{"a": 1, "b": 2');
Trying to insert an invalid JSON doc will elevate an error, and the entire report is not going to be inserted/up to date.
Looking out JSON Paperwork in MySQL JSON Column

With JSON MySQL features like JSON_CONTAINS() perform, you may examine if a JSON doc incorporates a particular worth. It returns 1 when a match is discovered. For instance:
SELECT * FROM `ebook` WHERE JSON_CONTAINS(tags, '["JavaScript"]');
The JSON_SEARCH() perform returns the trail to a worth inside a JSON doc. It returns NULL when there’s no match.
You too can specify whether or not that you must discover all or single matches by passing ‘one’ and ‘all’ flags alongside the search string (the place % matches any variety of characters and _ matches one character in an equivalent option to LIKE). For instance:
SELECT * FROM `ebook` WHERE JSON_SEARCH(tags, 'one', 'Java%') IS NOT NULL;
The JSON_TABLE() perform transforms JSON information right into a relational format for simpler querying:
SELECT *
FROM JSON_TABLE(
'[{"tag": "SQL"}, {"tag": "JSON"}]',
'$[*]' COLUMNS (tag VARCHAR(50) PATH '$.tag')
) AS tags_table;JSON Paths
A MySQL JSON question utilizing the JSON_EXTRACT() perform can retrieve particular values from a JSON doc primarily based on a specified path.
SELECT JSON_EXTRACT('{"id": 1, "web site": "SitePoint"}', '$.web site');All path definitions begin with a $ adopted by different selectors:
- A interval adopted by a reputation, comparable to $.web site
- [N] the place N is the place in a zero-indexed array
- The .[*] wildcard evaluates all members of an object
- The [*] wildcard evaluates all members of an array
- The prefix**suffix wildcard evaluates to all paths that start with the named prefix and finish with the named suffix
The next examples consult with the next JSON doc:
{
"a": ,
"b": 2,
"c": [, ],
"d": {
"e": ,
"f": 6
}
}
Instance paths:
- $.a returns 1
- $.c returns [3, 4]
- $.c[1] returns 4
- $.d.e returns 5
- $**.e returns [5]
You could possibly use the JSON extract MySQL perform to extract the identify and first tag out of your ebook desk effectively:
SELECT
title, tags->"$[0]" AS `tag1`
FROM `ebook`;
For a extra advanced instance, presume you’ve a consumer desk with JSON profile information. For instance:
| id | identify | profile |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Craig | { “electronic mail”: [“craig@email1.com”, “craig@email2.com”], “twitter”: “@craigbuckler” } |
| 2 | SitePoint | { “electronic mail”: [], “twitter”: “@sitepointdotcom” } |
You possibly can extract the Twitter identify utilizing a JSON path. For instance:
SELECT
identify, profile->"$.twitter" AS `twitter`
FROM `consumer`;
You could possibly use a JSON path within the WHERE clause to return solely customers with a Twitter account:
SELECT
identify, profile->"$.twitter" AS `twitter`
FROM `consumer`
WHERE
profile->"$.twitter" IS NOT NULL;
Modifying A part of a JSON Doc
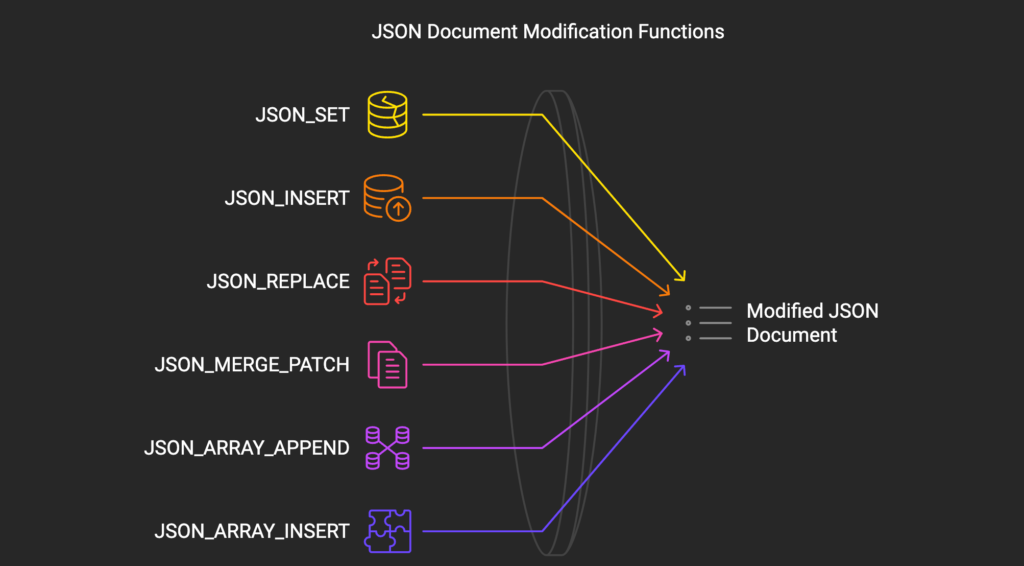
There are a number of MySQL features that modify components of a JSON doc utilizing path notation. These embrace:
- JSON_SET(doc, path, val[, path, val]…): Inserts or updates information within the doc.
UPDATE ebook SET tags = JSON_SET(tags, '$[0]', 'Up to date Tag'); - JSON_INSERT(doc, path, val[, path, val]…): Inserts information into the doc with out overwriting current values.
UPDATE ebook SET tags = JSON_INSERT(tags, '$[0]', 'New Tag'); - JSON_REPLACE(doc, path, val[, path, val]…): Replaces information within the doc.
UPDATE ebook SET tags = JSON_REPLACE(tags, '$[0]', 'Changed Tag'); - JSON_MERGE_PATCH(doc, doc[, doc]…): Merges two or extra JSON paperwork, changing current keys with values from subsequent paperwork.
UPDATE ebook SET tags = JSON_MERGE_PATCH(tags, '["technical"]') WHERE JSON_SEARCH(tags, 'one', 'JavaScript') IS NOT NULL; - JSON_ARRAY_APPEND(doc, path, val[, path, val]…): Appends values to the tip of an array.
UPDATE ebook SET tags = JSON_ARRAY_APPEND(tags, '$', 'New Tag'); - JSON_ARRAY_INSERT(doc, path, val[, path, val]…): Inserts values at a particular place inside a JSON array.
UPDATE ebook SET tags = JSON_ARRAY_INSERT(tags, '$[0]', 'Inserted Tag'); - JSON_REMOVE(doc, path[, path]…): Removes information from the doc.
UPDATE ebook SET tags = JSON_REMOVE(tags, '$[1]'); - JSON_PRETTY(val): Fairly-prints JSON paperwork for higher readability.
SELECT JSON_PRETTY('{"identify": "SitePoint", "tags": ["MySQL", "JSON"]}');
For instance, if you wish to add a “technical” tag to any ebook that already has a “JavaScript” tag, you need to use JSON_MERGE_PATCH() perform:
UPDATE ebook
SET tags = JSON_MERGE_PATCH(tags, '["technical"]')
WHERE JSON_SEARCH(tags, 'one', 'JavaScript') IS NOT NULL;Additional Data
The MySQL documentation supplies detailed details about MySQL JSON information kind and the related JSON features.
Once more, I urge you to not use JSON except it’s completely mandatory. You could possibly emulate a complete document-oriented NoSQL database in MySQL, however it will negate many advantages of SQL, and it’s possible you’ll as nicely swap to an actual NoSQL system!
That stated, JSON information sorts would possibly save effort for extra obscure information necessities inside an SQL software.
FAQs on Working With JSON Information in MySQL
Can You Use JSON in MySQL?
MySQL helps JSON by providing a JSON information kind for storing JSON-formatted information in columns. Ranging from MySQL 5.7.8, you may create tables with JSON columns, permitting you to insert, replace, and question JSON information utilizing SQL. MySQL supplies a spread of JSON features to work with JSON information inside these columns, enabling extraction, modification, and manipulation.
Moreover, you need to use JSON information in SQL queries, changing it to relational information when wanted utilizing features like JSON_TABLE. Nevertheless, it’s essential to know that MySQL is basically a relational database, and its JSON information kind assist is meant to facilitate working with JSON information inside a relational context relatively than being a full-fledged NoSQL JSON database.
As outlined within the article above, simply because you may retailer JSON, it doesn’t imply that you need to: Normalization is a method used to optimize the database construction. The First Regular Type (1NF) rule governs that each column ought to maintain a single worth — which is damaged by storing multi-value JSON paperwork.
Is It OK To Retailer JSON in MySQL?
It’s okay to retailer JSON in MySQL for situations like:
- Semi-structured or dynamic information that doesn’t match nicely in a inflexible schema.
- Customized attributes the place relational design could be inefficient.
- Integration with JSON-based APIs for storing payloads or logs.
Nevertheless, JSON ought to not change normalized relational storage for structured and regularly queried information. Whereas MySQL 9.1 improves JSON performance with options like purposeful indexes and JSON_TABLE, JSON operations should still introduce overhead for big datasets or advanced queries.
How To Use JSON in a MySQL Question?
You need to use JSON in MySQL queries by using MySQL’s JSON features. These features allow you to extract, manipulate, and question JSON information saved in JSON columns or JSON-formatted strings inside your database. To entry JSON information inside a JSON column, use the -> operator adopted by the trail to the specified JSON ingredient.
JSON features like JSON_EXTRACT, JSON_SET, and JSON_OBJECTAGG help you filter, modify, combination, and work with JSON information. You too can filter rows primarily based on JSON values utilizing the WHERE clause. MySQL’s JSON capabilities present a flexible option to work together and manipulate a JSON object instantly inside your database queries.
When To Use JSON in MySQL?
You need to use JSON in MySQL for the next situations:
- Semi-structured information: Use JSON when coping with unpredictable or sparse fields (e.g., customized attributes).
- Dynamic schemas: JSON supplies flexibility when information necessities change regularly.
- Hierarchical or nested information: JSON helps information with parent-child relationships or arrays.
- API integration: Retailer payloads, responses, or logs as JSON paperwork.
Nevertheless, keep away from JSON for:
- Regularly queried fields that require indexing (purposeful indexes may help, however relational design is commonly sooner).
- Strictly relational information requiring normalization.
- Conditions the place advanced querying on JSON paths would degrade efficiency.
How To Retailer JSON Information in MySQL?
To retailer JSON information in MySQL, you’ve two major choices. First, you need to use the JSON information kind launched in MySQL to create a desk with a JSON column. This methodology supplies structured storage and higher question efficiency for JSON information.
Alternatively, you may retailer JSON information as textual content in an everyday VARCHAR or TEXT column. This method is appropriate once you primarily must retailer and retrieve JSON information with out advanced database operations.
How Do You Index JSON Information in MySQL?
When you can not instantly index a JSON column, MySQL lets you create purposeful indexes on generated columns derived from JSON values.
For instance, to index the primary ingredient of a JSON array:
ALTER TABLE ebook
ADD COLUMN first_tag VARCHAR(50) AS (JSON_UNQUOTE(tags->'$[0]')),
ADD INDEX idx_first_tag (first_tag);This method improves question efficiency for regularly accessed JSON paths.
Ought to You Use MySQL or a NoSQL Database for JSON Information?
It is dependent upon your challenge necessities:
- Select MySQL should you want relational storage with occasional JSON dealing with for semi-structured information, customized attributes, or hierarchical information inside a relational mannequin.
- Select a NoSQL database (like MongoDB) in case your challenge entails in depth JSON storage, versatile schemas, and document-based operations as the first use case.
MySQL’s JSON assist is superb for hybrid workloads however can not totally change a purpose-built NoSQL database for doc storage.
How Do You Extract Particular Values From a MySQL JSON Discipline?
To extract particular values from a MySQL JSON area, use the JSON_EXTRACT() perform or the shorthand -> operator.
SELECT JSON_EXTRACT(tags, '$[0]') AS first_tag FROM ebook;
SELECT tags->'$[0]' AS first_tag FROM ebook;How Do You Question and Filter Information in a MySQL JSON Discipline?
To question and filter information saved in a MySQL JSON area, you need to use features like JSON_CONTAINS() and JSON_SEARCH(). You too can use JSON_EXTRACT() to retrieve particular values for additional filtering.
SELECT * FROM ebook
WHERE JSON_CONTAINS(tags, '["JavaScript"]');
SELECT * FROM ebook
WHERE JSON_SEARCH(tags, 'one', 'Java%') IS NOT NULL;
SELECT * FROM ebook
WHERE JSON_EXTRACT(tags, '$[0]') = 'JavaScript';










