Merely conforming to cybersecurity requirements, reminiscent of ISO/IEC 27001, or complying with regulatory necessities, reminiscent of PCI DSS, will not robotically make an enterprise’s safety full, efficient or economical. Assembly a standardized management baseline would possibly examine compliance containers, however creating a powerful risk-based technique, constructing a resilient working setting and hardening in opposition to evolving cyberthreats requires extra.
This hole — the distinction between the naked minimal and a strategic, formalized, resilience-based program — is what risk-based safety is all about. A risk-based strategy incorporates details about the group — its objectives, essential property, context, threats — into safety planning. It ensures assets are used optimally, context-specific circumstances are accounted for, and that actual threats tie on to deployed countermeasures.
Let us take a look at what a risk-based safety technique entails and 5 steps safety practitioners ought to comply with when creating their plan.
What’s risk-based safety?
Safety practitioners know that danger is a operate of two components:
- Impression. How unhealthy a given final result will likely be.
- Chance. The chance of that final result taking place.
A risk-based safety program is one which accounts for each components in its scope and planning: from management choices and governance to program administration and budgetary selections — and every thing in between.
On the floor, accounting for danger in a safety program sounds apparent. In apply, it is hardly ever the default strategy. Many organizations construct their safety packages by aligning to particular management units quite than precise danger circumstances. By design, compliance frameworks deal with whether or not given controls exist as an alternative of whether or not they’re warranted, environment friendly or aligned with precise circumstances.
Danger-based is commonly not the default as a result of it requires extra data and planning than simply specializing in a inventory catalog of controls. At a minimal, it requires data of the next:
- Threats. Understanding who would possibly assault the group, their motivation and the way they could achieve this.
- Vulnerabilities. Understanding the susceptibility of the setting to hurt, from IT programs to operational know-how.
- Belongings. Understanding how property assist the enterprise to precisely assess affect.
- Relative criticality. Understanding which property are essential.
- Danger urge for food. Understanding what the group views as an acceptable danger tolerance.
Many organizations haven’t got these particulars. Or in the event that they do, they know them solely on the most elementary degree. Acquiring this data is barely step one. The knowledge then must be systematically analyzed to assist actionable decision-making.
Although tough, there are important advantages to doing this:
- Accounting for safety outcomes lets organizations develop sensible, life like objectives that assist the organizational mission.
- Accounting for useful resource use allows extra environment friendly funding and finances utilization.
- Accounting for threats and vulnerabilities means higher efficiency at stopping cyberattacks and information breaches and realizing that noncompliance is itself a danger, too.
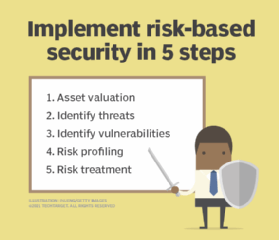
A risk-based safety program takes work however just isn’t essentially tough to arrange. There are 5 key steps to implementing a risk-based safety program that take larger time funding on the entrance finish, however the rewards — each in value and time financial savings — greater than make up for it over the long run.
Step 1. Asset valuation
Step one is to know the worth of organizational property. To do that, practitioners should know two issues:
- What property exist. This entails sustaining a whole, correct and present stock of all property, together with know-how and information property.
- The worth of these property. This implies understanding the significance of the property to the group — not simply their alternative value. The enterprise criticalities of processes that property assist should not all the time equal. To grasp the worth, assess property within the context of who makes use of them, what enterprise processes they assist, alternative prices, operational and enterprise impacts of downtime, and so forth.
There may be important overlap between understanding asset criticality for danger evaluation and doing so for enterprise continuity. The truth is, one productive approach is to mix the asset discovery and inventorying phases of danger evaluation with enterprise affect assessments, simply as groups would possibly do in furtherance of enterprise continuity planning.
Step 2. Establish threats
Along with understanding property, practitioners additionally have to know the way these property could be attacked. This implies realizing who — or what — may disrupt, affect or in any other case compromise these property.
Establish who would possibly wish to steal or injury the property, in addition to why and the way they could do it. This might embody opponents, hostile nations, disgruntled workers or purchasers, terrorists and activists, and nonhostile threats, reminiscent of untrained or negligent workers. Additionally, contemplate the specter of pure disasters, reminiscent of floods, fires and tornadoes. Lastly, consider nonenvironmental and nonintentional conditions, together with pandemics or geopolitical upheavals.
Assign every recognized risk a risk degree primarily based on its probability of occurring. This requires enter from enterprise groups so as to add sector-specific data to the safety workforce’s personal risk assessments. Think about incorporating further information, reminiscent of business risk intelligence or different details about the risk panorama.
Step 3. Establish vulnerabilities
A vulnerability is a weak point that may be exploited to steal, injury or in any other case negatively have an effect on key property. For an undesirable safety final result to happen, practitioners want two issues: an actor — e.g., a hacker, a pure catastrophe, and so forth. — and a pathway for that actor to have an effect on the enterprise. Since each should be current for an undesirable final result to happen, practitioners want to research each.
Throughout this step, determine the vulnerabilities within the enterprise setting. This permits practitioners to evaluate which threats are most germane to the corporate and to pick out the optimum controls to mitigate these particular threats. Think about using the next instruments:
Moreover, account for bodily vulnerabilities. Are perimeters safe and patrolled? Are fireplace extinguishers commonly checked? Are backup mills examined? Additionally contemplate vulnerabilities related to workers, contractors and suppliers, together with their susceptibility to social engineering assaults. As soon as once more, collaborate with enterprise groups to search out and account for vulnerabilities particular to enterprise processes in use.
Step 4. Danger profiling
After figuring out the group’s property, threats and vulnerabilities, start danger profiling. This course of evaluates current controls and safeguards and measures danger for every asset-threat-vulnerability mixture. Practitioners ought to systematically assess every asset for susceptibility to every risk utilizing the vulnerabilities to information how probably every is.
Do that formally or informally, quantitatively or qualitatively. There are a whole bunch of approaches to select from, together with the next:
Base scores on the risk degree and the affect on the group ought to the chance happen. Think about using a qualitative strategy to attain every potential final result throughout a scale of low, medium and excessive primarily based on probability and affect. Or use financial calculations — e.g., annualized loss expectancy. It is much less vital how practitioners do it than that they do it.
Learn extra on community safety danger rankings.
Step 5. Danger therapy and remediation
The final and arguably most vital step is to deal with the issues recognized. Dangers vary from these low sufficient that the enterprise can settle for them with out antagonistic affect to dangers which can be so extreme they should be averted in any respect prices.
To know the distinction, practitioners should perceive the group’s tolerance for danger — i.e., how prepared it’s to tackle danger contemplating the potential outcomes.
Assess every danger in opposition to the chance tolerance. For these thought-about unacceptable, resolve dispense with them. Many danger administration guides discuss 4 choices:
- Avoidance. Put the group out of hurt’s method completely — e.g., ceasing the enterprise course of {that a} given danger impacts.
- Mitigation. Put a management or countermeasure in place to scale back the probability of an final result.
- Switch. Use a mechanism — e.g., insurance coverage — to shift danger dynamics to a different.
- Acceptance. Resolve to dwell with the chance as-is.
Doc every resolution and the explanations that led to it. Repeat the method for every risk state of affairs to appropriately apply assets to the dangers recognized to have essentially the most important impact on the enterprise.
As soon as carried out, check to make sure any new safety controls carry out as meant.
Keep in mind, risk-based safety just isn’t a one-and-done train; practitioners ought to set up a cadence of validation over time. Danger profiles change continuously — the enterprise will adapt the way it does issues, applied sciences will change, and threats will evolve. Practitioners ought to periodically revalidate every thing they beforehand assessed. For this reason detailed data of choices made are so vital.
Ideas for first-timers implementing risk-based safety
Getting applicable assist is paramount. In some circumstances, govt assist would possibly suffice, others would possibly require board-level approval. Attempt to construct a risk-aware tradition the place administration buys in and helps practitioners propagate it all through the group.
Stakeholder enter is crucial. Every risk-based safety step exhibits how essential enterprise affect is, however keep in mind that data sharing cuts each methods, so plug enterprise workforce members into the efforts. Danger mitigation choices can have a critical impact on operations, which safety groups won’t absolutely perceive. A risk-based tradition pays dividends as a result of enterprise groups can talk danger data proactively quite than having to be requested.
Attaining complete safety in a corporation is inconceivable, and budgets aren’t limitless. It is vital to deploy assets and experience intelligently and cost-effectively. A great way to do that is to maneuver to a risk-aware mannequin. Whereas requiring some further elbow grease to implement, these steps may help transfer organizations in that route.
Ed Moyle is a technical author with greater than 25 years of expertise in data safety. He’s a accomplice at SecurityCurve, a consulting, analysis and schooling firm.
Michael Cobb contributed to this text.