Collections in Java type the spine of environment friendly information administration and manipulation. Whether or not you’re dealing with a set record in Java for small-scale duties or managing huge datasets, Java Collections streamline these duties by offering pre-defined assortment framework lessons and interfaces.
This assortment framework in Java tutorial explains collections in Java intimately to assist freshmen and seasoned builders.
Key Takeaways
- Study the distinction between the Collections Framework and Assortment Interface, together with their information administration and manipulation roles. Get Java collections defined step-by-step to simplify ideas for freshmen.
- Examine the Java collections subjects like lists, units, maps, and algorithms for environment friendly information dealing with.
- Make the most of Streams API and Lambda Expressions for functional-style operations similar to filtering, mapping, and lowering information.
- Apply sorting, shuffling, looking out, and reversing algorithms to streamline widespread operations in information processing.
- Discover extra assortment examples in Java, together with customized implementations and real-world use instances to deepen understanding.
- Use concurrent collections like ConcurrentHashMap for multi-threaded environments and immutable collections (Java 9+) for fixed datasets.
- Use Java collections in Java applications to deal with caching, occasion processing, and information storage with real-world examples.
What Is Assortment and Framework in Java?
In Java, a set is an interface representing a bunch of objects, referred to as parts, which are saved and manipulated as a single unit. Collections in Java are type-safe when applied with generics, making certain parts are of the identical sort. Though uncooked varieties permit heterogeneous information, their use is deprecated and discouraged in fashionable Java.
The Java Collections Framework gives a complete structure with interfaces, lessons, algorithms, and utility strategies for managing collections. It helps thread-safety by way of concurrent collections (e.g., ConcurrentHashMap) and immutability utilizing Java 9+ strategies like Listing.of() and Set.of().
The framework simplifies information storage, retrieval, and processing duties with reusable elements that enhance effectivity, flexibility, and interoperability with Java APIs.
Collections Framework Vs. Assortment Interface
The Collections Framework and Assortment Interface are distinct however interconnected elements of Java’s information administration system:
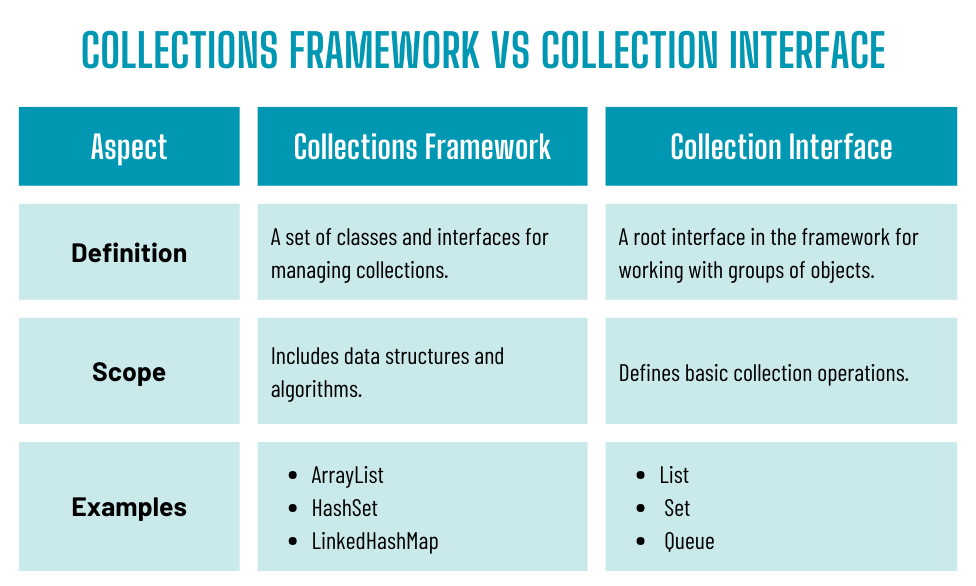
Assortment Interface
The Assortment Interface acts because the blueprint, defining core operations similar to including, eradicating, and checking for parts. It serves as a superinterface for Listing, Set, and Queue. Whereas it doesn’t present direct implementations, it ensures consistency throughout several types of collections, facilitating polymorphism and suppleness in dealing with information.
Collections Framework
Supplies a whole structure for managing information by way of lessons, interfaces, and algorithms. Contains implementations like ArrayList, HashSet, and TreeMap together with Java assortment framework lessons that deal with sorting, looking out, and shuffling. For a deeper understanding, the Java assortment framework intimately explains the position of every class and interface in information processing.
Why Use the Collections Framework?
There are a number of explanation why you must think about using the Java Collections Framework.
1. Effectivity
Pre-built algorithms improve efficiency by offering optimized options for sorting, looking out, and manipulation.
Listing<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(4, 2, 8, 6);
Collections.kind(numbers);
System.out.println(numbers); 2. Flexibility
Helps numerous information buildings, similar to lists, units, and maps, to satisfy numerous software necessities.
Map<String, String> messages = new HashMap<>();
messages.put("user1", "Howdy");
messages.put("user2", "Hello");
System.out.println(messages.get("user1")); 3. Reusability
Builders can leverage pre-defined lessons and interfaces, considerably lowering growth time. It additionally permits builders to customise information buildings by extending present lessons or implementing interfaces.
class CustomList<T> extends ArrayList<T> {
@Override
public boolean add(T ingredient) {
if (!this.accommodates(ingredient)) {
return tremendous.add(ingredient);
}
return false;
}
}4. Scalability
The framework is appropriate for small-scale applications in addition to giant, enterprise-level functions. It helps dynamic resizing (e.g., ArrayList and HashMap) and thread-safe collections (e.g., ConcurrentHashMap) for enterprise-level necessities.
Listing<Integer> information = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
information.parallelStream().forEach(System.out::println);5. Robustness
Framework gives fail-fast iterators and concurrent collections (e.g., ConcurrentHashMap) to forestall information corruption in multi-threaded environments. This Java assortment tutorial in depth covers scalable options like parallel streams for giant datasets.
Listing<String> immutableList = Listing.of("A", "B", "C");
immutableList.add("D"); 6. Newbie-Pleasant
The framework gives instruments and strategies, making it an excellent assortment in Java for freshmen to study step-by-step. Its constant design and intensive assist for widespread operations simplify the training curve.
The Java Collections Framework Construction and Hierarchy
The Java Collections Framework gives a structured structure for effectively storing, managing, and manipulating information. So, let’s begin with the fundamentals of collections in Java to construct a robust basis earlier than diving into superior examples.
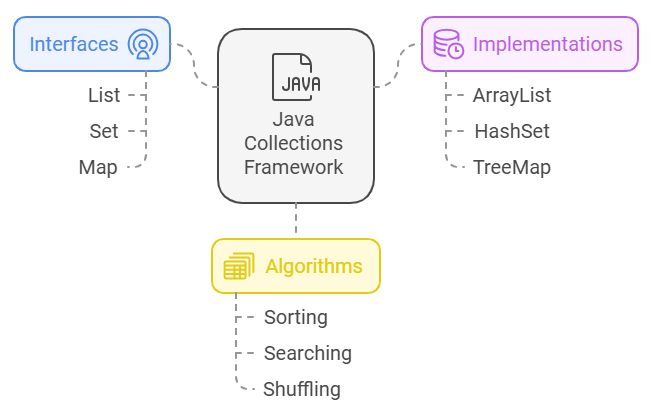
1. Interfaces
Interfaces outline the construction and conduct of several types of collections. They act as blueprints for a way information ought to be organized and accessed. Listed below are some well-liked interface assortment examples in Java.
Core Assortment Interfaces:
Assortment is the foundation interface for many collections, defining strategies like add(), take away(), and measurement().
Assortment<String> gadgets = new ArrayList<>();
gadgets.add("Item1");
System.out.println(gadgets.measurement()); Listing is an ordered assortment that enables duplicates and helps index-based entry (e.g., ArrayList).
Listing<String> record = new ArrayList<>();
record.add("A");
record.add("B");
System.out.println(record.get(1)); Set is an unordered assortment that don’t permit duplicates (e.g., HashSet).
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(1);
set.add(1);
System.out.println(set.measurement()); Queue follows FIFO (First-In-First-Out) order. It’s preferrred for process scheduling (e.g., LinkedList).
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add("Task1");
queue.add("Task2");
System.out.println(queue.ballot()); Map shops key-value pairs (e.g., HashMap). Though it isn’t a part of the Assortment interface however is included within the framework.
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("A", 1);
System.out.println(map.get("A")); Specialised Assortment Interfaces:
Deque is a double-ended queue that enables insertions/removals at each ends.
Deque<String> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.addFirst("A");
deque.addLast("B");
System.out.println(deque.removeFirst()); SortedSet, and NavigableSet deal with sorted parts and assist vary queries.
SortedSet<Integer> sortedSet = new TreeSet<>();
sortedSet.add(10);
sortedSet.add(5);
System.out.println(sortedSet.first()); SortedMap, and NavigableMap handle sorted key-value pairs and assist navigation strategies.
NavigableMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(1, "One");
map.put(2, "Two");
System.out.println(map.firstEntry()); 2. Implementations / Concrete Courses
Concrete lessons present particular implementations for every interface, providing flexibility and optimized efficiency based mostly on information dealing with necessities.
ArrayList is a reusable array that helps quick random entry (O(1)) and O(n) insertion/removing for center parts.
ArrayList<Integer> record = new ArrayList<>();
record.add(10);
System.out.println(record.get(0)); LinkedList is a doubly linked record, environment friendly for insertions/deletions (O(1)) however slower entry (O(n)).
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add("A");
linkedList.addFirst("B");
System.out.println(linkedList.getFirst()); HashSet is an unordered distinctive record that gives O(1) lookup utilizing hashing.
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("Apple");
System.out.println(set.accommodates("Apple")); TreeMap maintains sorted key-value pairs, and presents O(log n) efficiency.
TreeMap<String, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("A", 1);
System.out.println(map.firstKey()); 3. Algorithms / Utility Courses
The framework gives quite a lot of utility algorithms to function on collections, simplifying widespread duties like sorting, looking out, and shuffling. These can be found by way of the Collections class and are optimized for efficiency.
Sorting with Collections.kind() for ordering parts.
Listing<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(5, 3, 8, 2);
Collections.kind(numbers);
System.out.println(numbers); Looking out with Collections.binarySearch() for fast lookups.
int index = Collections.binarySearch(numbers, 5);
System.out.println(index); Shuffling with Collections.shuffle() to randomize order.
Collections.shuffle(numbers);
System.out.println(numbers); Reversing with Collections.reverse() for reversing ingredient order.
Collections.reverse(numbers);
System.out.println(numbers); Fashionable Enhancements
The most recent Java variations have launched some thrilling options for the Java Collections Framework.
Streams API
Stream API was launched in Java 8 to assist functional-style programming to course of information saved inside collections and arrays. It helps operations like filtering, mapping, and lowering.
Stream operations are chained in a pipeline, which improves readability and reduces boilerplate code. In addition they solely course of information when terminal operations like acquire() or forEach() are invoked. This minimizes computations for intermediate operations.
Instance on Filtering even numbers
Listing<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Listing<Integer> evenNumbers = numbers.stream()
.filter(n -> n % 2 == 0)
.acquire(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(evenNumbers); Streams can function in parallel mode to utilize multi-core processors for scalability. Additionally, streams use lambda expressions as a substitute of express loops, making the code extra concise and simpler to learn.
Parallel Streams
Parallel Streams prolong the Streams API by enabling multi-threaded processing of knowledge. This characteristic is extraordinarily helpful for processing giant datasets.
In parallel streams, duties are mechanically divided into subtasks and executed concurrently utilizing the Fork/Be part of framework:
Listing<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
numbers.parallelStream().forEach(System.out::println);Parallel streams don’t keep order. So, they’re finest for duties when the ordering just isn’t necessary. Additionally, it makes use of all out there processor cores by default, making it preferrred for CPU-bound duties like batch processing, filtering, or large-scale transformations.
Immutable Collections (Java 9)
Immutable collections had been launched in Java 9 to simplify the creation of read-only collections that can’t be modified after initialization. Immutable collections might be created utilizing manufacturing facility strategies like Listing.of(), Set.of(), and Map.of() for fast initialization:
Listing<String> immutableList = Listing.of("A", "B", "C");
System.out.println(immutableList);
immutableList.add("D"); These collections don’t permit null values, making certain information integrity and lowering potential errors attributable to null references.
Customized Implementations
Creating customized implementations of Java Collections permits builders to tailor information buildings to particular wants, enhancing performance and efficiency. That is particularly helpful when default implementations like ArrayList or HashSet don’t absolutely meet your software’s necessities. Under are steps, examples, and finest practices for implementing customized collections in Java.
Why Create Customized Implementations?
Customized implementations are preferrred when built-in collections can not fulfill particular software wants. They permit builders so as to add specialised conduct, enhance efficiency, or implement domain-specific constraints.
- Add customized validation, ordering, or filtering logic.
- Tailor information buildings for distinctive software necessities.
- Align collections with enterprise logic or area constraints.
1. Dealing with Customized Objects in Collections
If customized objects are added to the gathering, builders ought to override equals() and hashCode() strategies for correct comparability and uniqueness checks. Under instance highlights the significance of defining equality and hashcode logic when storing customized objects in collections like HashSet or HashMap.
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;
class Worker {
String id;
String identify;
Worker(String id, String identify) {
this.id = id;
this.identify = identify;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Worker worker = (Worker) o;
return id.equals(worker.id);
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id);
}
}
public class CustomObjectExample {
public static void principal(String[] args) {
HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<>();
workers.add(new Worker("101", "Alice"));
workers.add(new Worker("102", "Bob"));
workers.add(new Worker("101", "Alice"));
System.out.println(workers.measurement());
}
}2. Thread-Secure Customized Implementations
If multi-threading is required, builders ought to think about thread-safe approaches. This ensures your customized implementation doesn’t fail in concurrent environments.
- Use Collections.synchronizedList() for thread security.
- Use ConcurrentHashMap or CopyOnWriteArrayList for higher scalability.
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
class ThreadSafeListExample {
public static void principal(String[] args) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> record = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
record.add("Java");
record.add("Python");
for (String lang : record) {
record.add("C++");
}
System.out.println(record);
}
}Though these customized implementations offer you freedom, ensure to:
- Prolong solely when built-in collections can not meet necessities.
- Make sure the customized implementation helps customary strategies like iterator() and measurement().
- Guarantee sort security for higher reusability.
- Check the implementation towards customary collections for efficiency analysis.
- Clearly doc any customized logic, particularly deviations from customary conduct.
Finest Practices
Adopting finest practices whereas working with Java Collections ensures environment friendly, dependable, and maintainable code. Under are pointers for leveraging the facility of Java Collections.
1. Select the Proper Assortment Kind
- Use ArrayList for quick random entry and LinkedList for frequent insertions/deletions.
- Use HashSet for distinctive parts with out order and TreeSet for sorted parts.
- Use HashMap for quick key-value lookups and TreeMap for sorted keys.
2. Use Generics
Generics guarantee sort security, lowering runtime errors and making code cleaner:
Listing<String> record = new ArrayList<>();
record.add("Java"); 3. Keep away from ConcurrentModificationException
Use fail-safe iterators from the java.util.concurrent bundle for concurrent environments.
Map<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
map.put("Key1", "Value1");
map.forEach((key, worth) -> map.put("Key2", "Value2"));
System.out.println(map); 4. Leverage Immutable Collections
Use manufacturing facility strategies like Listing.of() for read-only collections.
Listing<String> immutableList = Listing.of("A", "B", "C");
Benefits of the Java Assortment Framework
The Java Collections Framework (JCF) is a cornerstone of contemporary Java programming, providing pre-built lessons and interfaces for environment friendly information administration. Listed below are some key adavantages of utilizing JCF.
- Contains ArrayList, HashSet, and TreeMap, saving time for builders seeking to discover all Java collections intimately. To simplify growth additional, the Java collections bundle gives utility strategies and pre-built algorithms, making information manipulation extra environment friendly.
- Generics forestall runtime errors by imposing sort constraints.
Listing<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>();
numbers.add(10);
- Use ConcurrentHashMap for secure multi-threaded entry.
- Works seamlessly with different Java APIs like Streams.
- Builders can create customized implementations tailor-made to particular wants.
Language Comparability

Evaluating Java Collections with information buildings and algorithms in different programming languages highlights its distinctive options.
Python vs. Java Collections
Lists
Python’s record is just like Java’s ArrayList. It helps dynamic resizing and index-based entry. Nonetheless, Java’s ArrayList is type-safe with generics, whereas Python’s record permits blended varieties.
Dictionaries
Python’s dictionary matches Java’s HashMap. However Python gives extra versatile operations similar to comprehension-based initialization and default values by way of collections.defaultdict.
Units
Each Python’s set and Java’s HashSet implement uniqueness. However Python’s set helps operations like unions (|) and intersections (&) immediately by way of operators.
Tuples vs. Immutable Collections
Python’s tuple represents immutable sequences, corresponding to Java’s immutable collections launched in Java 9 (Listing.of() and Set.of()).
C++ STL vs. Java Collections
Vectors
C++ std::vectoris equal to Java’s ArrayList, each providing dynamic resizing. Java programming language gives extra thread-safe options, similar to Vector.
Maps
C++ std::map is corresponding to Java’s TreeMap for sorted key-value pairs. However Java additionally helps hash-based maps (HashMap) and concurrent maps (ConcurrentHashMap) for multithreading.
Queues
C++ std::queue and Java’s Queue (e.g., LinkedList and PriorityQueue) provide comparable FIFO conduct, however Java’s Deque gives added flexibility with double-ended operations.
JavaScript vs. Java Collections
Arrays
JavaScript’s Array is versatile and dynamic however lacks strict type-checking, in contrast to Java’s ArrayList with generics.
Objects vs. Maps
JavaScript’s plain objects ({}) usually act as key-value shops however lack ordering ensures. Java’s HashMap and TreeMap present ordered or unordered key-value storage with sort security.
Units
JavaScript’s Set matches Java’s HashSet for uniqueness however doesn’t present superior options like thread security.
Actual-World Use Instances
Java Collections play a pivotal position in numerous real-world functions. Listed below are some sensible situations:
- Caching: Use HashMap to retailer continuously accessed information.
Map<String, String> cache = new HashMap<>();
cache.put("user1", "data1");
System.out.println(cache.get("user1"));- Occasion Dealing with: Queue for scheduling and processing occasions.
- Knowledge Storage: Use ArrayList or LinkedList for dynamic information storage.
- Concurrent Processing: Use ConcurrentHashMap for thread-safe operations.
Conclusion
Java Collections gives a robust framework for managing and manipulating information effectively. Builders can construct scalable and high-performance functions utilizing built-in implementations or creating customized ones.
Java programmers can guarantee their options stay sturdy and future-proof by following finest practices and using fashionable enhancements like Streams API and immutable collections.
FAQs on Collections in Java
What Are the Forms of Collections in Java?
Java collections embrace Listing, Set, Queue, and Map interfaces. These core Java assortment interfaces signify particular information buildings, similar to dynamic arrays, doubly linked lists, and hash tables. They supply a unified structure for manipulating collections within the Java Collections Framework, overlaying Java collections fundamentals for freshmen.
How Do I Select the Proper Assortment for My Use Case?
Selecting the suitable assortment interface is dependent upon your particular information construction and operations:
- Use ArrayList (a primary implementation of dynamic arrays) for quick, random entry to parts in an ordered assortment.
- Use LinkedList (a doubly linked record) for frequent insertions and deletions.
- Use HashMap (a category that implements the Map interface) for environment friendly key-value storage and retrieval.
The above Java collections full tutorial explores these selections with sensible situations and examples.
What Is the Main Distinction Between Fail-Quick and Fail-Secure Iterators?
Fail-fast iterators throw ConcurrentModificationException when the whole assortment is modified throughout iteration. These are widespread in customary assortment interfaces like Listing interface and Set interface.
Fail-safe iterators, usually from the concurrent bundle, function on a cloned copy of the gathering, making certain secure iteration even when modifications happen.
Are Java Collections Thread-Secure?
Not all Java collections are thread-safe. To make sure thread security, use lessons from the concurrent bundle, similar to ConcurrentHashMap, or wrap present assortment implementations with synchronized wrappers. For instance, Collections.synchronizedList ensures secure entry to a listing in multi-threaded environments.
Are Java Collections Appropriate for Rookies?
Sure, Java Collections are beginner-friendly on account of their structured design and predefined strategies. This text is a freshmen information for Java assortment, providing step-by-step explanations and examples to simplify studying.
How Can I Study Java Collections with Sensible Examples?
Builders can study Java Collections successfully by working by way of pattern applications demonstrating real-world situations. This Java collections tutorial with instance applications covers sensible implementations similar to sorting, filtering, and information processing.
How Does the Collections Framework Enhance Efficiency?
The Collections Framework reduces programming effort and enhances efficiency by way of:
- Optimized algorithms like binary search and fast kind are applied in customary Java assortment lessons.
- Environment friendly information buildings like HashMap and TreeSet.
- Stream API permits functional-style operations similar to filtering, mapping, and lowering for the whole assortment.
This reusable structure helps handle and manipulate numerous information buildings effectively.
What Are the Variations Between Listing and Set in Java?
Listing interfaces signify an ordered assortment of parts, permitting duplicate parts. It’s preferrred for particular information buildings like process lists.
Set interfaces guarantee uniqueness by disallowing duplicates however don’t assure order. They’re appropriate for distinctive datasets like IDs or tags.
How Does the Map Interface Differ from Different Collections?
In contrast to the Listing, Set, or Queue interfaces, the Map interface shops key-value pairs that maintain standalone parts. Maps are appropriate for storing configurations or caching the place environment friendly retrieval by a secret is essential. Courses like HashMap and TreeMap signify collections particularly designed for this goal.
What Are Immutable Collections, and Why Are They Essential?
Immutable collections, launched in Java 9, can’t be modified after creation. They forestall unintended modifications and are perfect for storing fixed datasets, like configuration recordsdata or settings. Builders create immutable collections utilizing static strategies to cut back programming errors and guarantee information consistency.
How Are Collections Built-in with Java Streams?
Java Streams gives a functional-style API for processing Java collections. They allow filtering, mapping, and lowering operations with out modifying the unique assortment. For instance, utilizing a Stream API, you may course of a specified assortment to calculate sums or discover the pure ordering of its parts with minimal code.
What Is the Distinction Between Comparable and Comparator in Java?
Comparable is used to outline the pure ordering of objects in a set. It requires the category to implement the compareTo() methodology. Use Comparable when sorting logic is fastened (e.g., sorting workers by ID).
Comparator is used to outline customized sorting logic exterior the category. It requires implementing the examine() methodology. Use Comparator whenever you want a number of sorting standards (e.g., kind workers by identify, then by wage).
What Is the Distinction Between ArrayList and LinkedList in Java?
ArrayList relies on a dynamic array and permits quick random entry utilizing indices, making it preferrred for read-heavy operations. Use ArrayList when frequent retrieval is required.
LinkedList is applied as a doubly linked record, providing sooner insertions and deletions however slower random entry. Use LinkedList when frequent insertion or deletion is required.
What Are PriorityQueue and Deque, and How Are They Used?
PriorityQueue is a queue that orders parts based mostly on their pure ordering or by a customized comparator supplied throughout initialization. It’s usually utilized in situations requiring priority-based processing, similar to process scheduling or shortest-path algorithms.
Deque permits insertion and removing at each ends of the queue. It’s Helpful for stack-like (LIFO) or queue-like (FIFO) conduct.










