Constructing Moral and Clear AI Frameworks
Synthetic intelligence shapes choices in enterprise, healthcare and authorities and we should be constructing moral and clear AI frameworks. Individuals fear about bias, opacity and information misuse. Speedy AI deployment with out moral planning may cause reputational hurt and authorized points. Accountable AI governance ensures innovation advantages society and preserves equity.
Moral and accountable AI
Moral AI and accountable AI overlap however concentrate on completely different concepts. Moral AI addresses philosophical questions on equity, justice and social influence. It makes use of ideas to look at how AI adjustments society. Accountable AI pertains to how organisations deploy AI. It focuses on accountability, transparency and compliance with legal guidelines. A hospital utilizing AI for diagnostics wants to observe algorithms to make sure honest remedy and clarify operations to regulators and sufferers.
Core ideas of moral AI
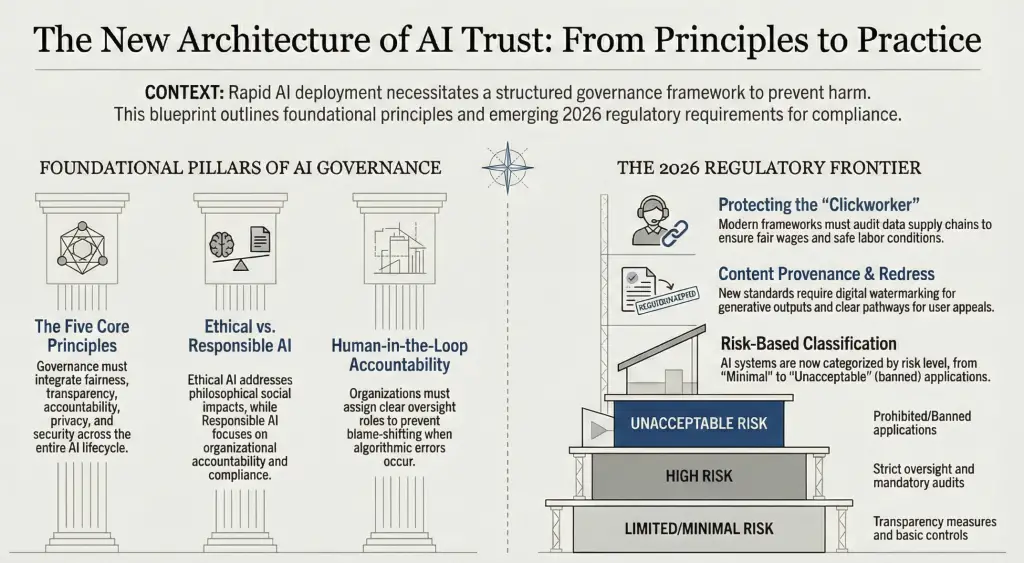
A robust governance framework makes use of 5 ideas: equity, transparency, accountability, privateness and safety. Equity means AI techniques should ship equal outcomes throughout protected teams. Builders have to set equity standards and carry out bias audits. Investigations into felony justice algorithms have proven that even seemingly impartial fashions can produce discriminatory outcomes if equity just isn’t outlined and examined.
Transparency requires organisations to reveal information inputs and algorithmic logic. Various groups ought to study coaching information and algorithms to identify hidden biases and clarify choices clearly. Transparency builds belief by serving to individuals perceive why a mannequin makes a suggestion. Accountability ensures that people stay liable for outcomes. AI techniques can’t take accountability; organisations should assign oversight roles and outline who solutions for errors. This prevents blame shifting and encourages cautious oversight.
Privateness protects private information utilized in coaching and deploying AI fashions. Organisations should use encryption, entry controls and anonymisation to maintain information secure. Additionally they have to adjust to information safety legal guidelines. Safety guards techniques in opposition to assaults and misuse. With out sturdy safety, attackers may manipulate information or fashions, undermining reliability and harming customers.
Governance frameworks and organisational roles
Ideas alone don’t assure moral AI. Organisations want structured governance frameworks that unify pointers, processes and roles throughout all enterprise models. These frameworks kind the premise for danger administration, documenting easy methods to determine, mitigate and monitor AI dangers. They flip summary values into sensible steps.
A complete framework ought to outline key roles. An AI governance council or ethics board units technique, oversees implementation and resolves points. Knowledge scientists and engineers develop fashions that observe the framework. Authorized and compliance officers guarantee alignment with legal guidelines. Enterprise homeowners are accountable for AI of their domains. Knowledge stewards handle information high quality and entry. Clear accountability ensures that every a part of the AI lifecycle has an proprietor.
Insurance policies and requirements should cowl all the AI lifecycle: information assortment, mannequin growth, validation, deployment, monitoring and retirement. Procedures ought to embrace bias mitigation, change administration and incident response plans. For example, an organisation may require common bias testing and unbiased audits for fashions affecting human choices. Setting these guidelines helps keep belief and consistency.
Aligning with world requirements
Accountable AI frameworks ought to align with worldwide pointers. Legal guidelines and ideas emphasise equity, accountability and transparency. They stress human oversight, technical robustness and non‑discrimination. Aligning insurance policies with exterior requirements prepares organisations for evolving rules.
Rising gaps and updates for 2026
New challenges have surfaced in 2025 and 2026 that the majority governance frameworks overlook. These gaps require particular consideration to make sure moral AI deployment.
Human labor and labor rights
AI fashions depend on massive volumes of labelled information supplied by human employees. Many of those “clickworkers” function in low‑revenue areas and face exploitation. Moral AI governance should embrace labor rights. Organisations ought to audit information provide chains, guarantee honest wages and secure working circumstances, and keep away from utilizing information labelled by compelled labour. Including a “Labor Rights” clause to produce chain insurance policies helps shield the individuals behind your AI.
Danger‑primarily based classification of AI techniques
Not all AI techniques pose the identical dangers. International rules, such because the European Union AI Act, classify AI purposes into 4 tiers: Unacceptable Danger, Excessive Danger, Restricted Danger and Minimal Danger. Unacceptable purposes are banned, whereas excessive‑danger techniques require strict oversight. Restricted danger techniques should embrace transparency measures, and minimal danger techniques want few controls. Naming the tiers in your insurance policies ensures groups apply the suitable necessities primarily based on the mission’s danger degree.
Content material provenance and output validation
Generative AI can produce hallucinations or deceptive content material. Authorized requirements now require “hallucination administration” and “watermarking” for generative fashions. Governance frameworks ought to embrace output validation to verify generated content material in opposition to trusted information. Watermarking embeds hidden markers in outputs to trace provenance and discourage misuse. These measures strengthen safety and transparency.
Legal responsibility and redress for AI choices
AI governance should deal with what occurs when techniques fail. People affected by an AI choice want a transparent pathway to enchantment and search treatment. A “Proper to Redress” part defines how customers can problem choices and acquire human assessment. Together with a devoted appeals course of ensures accountability and protects customers from hurt.
Implementation roadmap and detailed plan
To place accountable AI into observe, observe a structured plan:
- Determine all AI techniques utilized in your organisation. Doc their functions and influence.
- Consider information sources for every system. Notice information sensitivity and possession.
- Assess dangers by analysing potential biases, privateness points and compliance gaps.
- Set core ideas primarily based on equity, transparency, accountability, privateness and safety.
- Create a governance council with leaders from IT, compliance, authorized, ethics and enterprise models.
- Outline roles and obligations for creating, approving, deploying and monitoring AI techniques.
- Assemble an ethics board with exterior advisors or specialists to assessment excessive‑influence initiatives.
- Draft information administration insurance policies overlaying assortment, storage and anonymisation.
- Set up mannequin growth requirements requiring equity assessments, bias checks and explainability.
- Create documentation templates for coaching information sources, mannequin options and validation outcomes.
- Design an incident response plan for dealing with mannequin failures or moral breaches.
- Develop a mannequin registry that tracks fashions, homeowners, deployment standing and efficiency metrics.
- Combine governance checkpoints into mission workflows from design by deployment.
- Contain multidisciplinary groups together with ethicists and authorized specialists in design opinions.
- Implement transparency measures by offering clear explanations for AI choices and person‑dealing with documentation.
- Schedule common audits to assessment compliance, equity metrics and operational efficiency.
- Monitor fashions repeatedly utilizing metrics to detect drift, bias or anomalies.
- Retrain or retire fashions in the event that they fail to satisfy efficiency or moral requirements.
- Educate workers on moral AI ideas, dangers and compliance obligations.
- Promote a tradition of accountability by encouraging reporting of points with out concern of retaliation.
- Align insurance policies with evolving world rules and business pointers.
- Take part in business boards to remain knowledgeable about greatest practices and regulatory updates.
- Evaluation the framework recurrently and regulate primarily based on suggestions and altering necessities.
- Measure outcomes to find out whether or not governance reduces danger and will increase belief.
- Refine insurance policies and instruments primarily based on classes realized and technological advances.
- Assess labour circumstances in your information provide chain. Affirm that information annotators obtain honest wages and secure working circumstances.
- Assign danger tiers for every mission: Unacceptable, Excessive, Restricted or Minimal. Apply insurance policies primarily based on the tier.
- Validate generative outputs by automated checks. Add watermarking and hallucination detection to make sure integrity.
- Create an appeals course of for people harmed by AI choices. Present a transparent path for redress.
Conclusion
AI provides highly effective alternatives throughout many sectors, however unregulated use may cause hurt. By making use of equity, transparency, accountability, privateness and safety ideas and following a structured governance framework, organisations can deploy AI responsibly. Detailed insurance policies, properly‑outlined roles, common monitoring and alignment with world requirements create a reliable AI atmosphere. Accountable AI governance is a necessity for sustainable innovation and public confidence.










