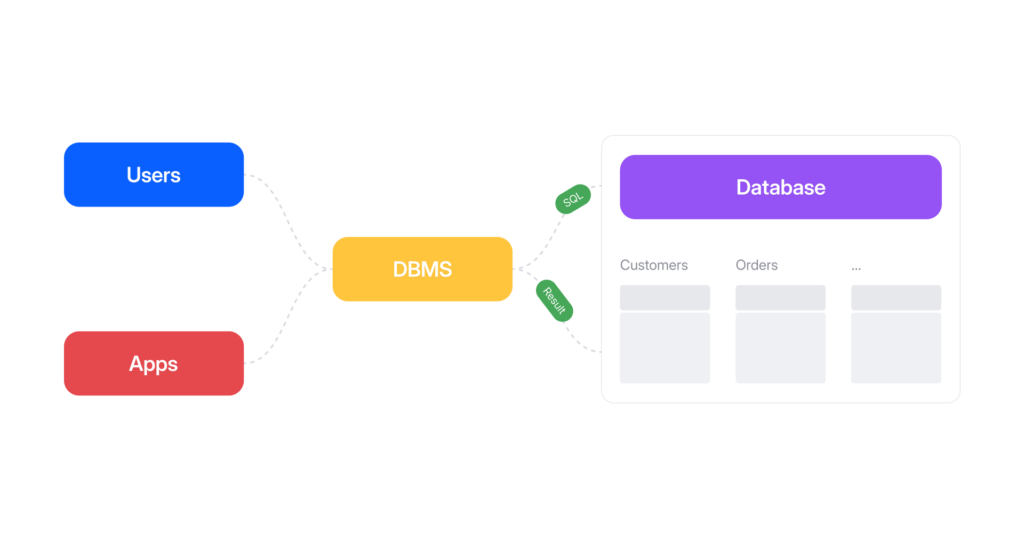
SQL (Structured Question Language) is a programming language that enables information administration and manipulation inside relational database administration methods. Nowadays, all small and huge enterprises are counting on SQL for his or her information storage and transformation. In most situations, studying solely primary instructions allows us to handle our databases successfully.
Key Takeaways
- SQL instructions are categorized into 5 classes akin to DDL, DML, DCL, DQL, and TCL, every serving particular database wants.
- SQL instructions vary from permitting primary queries akin to CREATE and UPDATE to incorporating advanced features akin to mixture features and becoming a member of tables to create advanced queries.
- Choosing the proper SQL dialect depends upon the applying necessities, price range, and integration capabilities.
- Builders can construct data-driven purposes by integrating SQL with programming languages and enterprise intelligence (BI) instruments to handle information and extract significant insights from it.
- Safe authentication strategies, entry management, and encryption shield the database from unauthorized entry.
What Are SQL Instructions?
SQL supplies a complete sql instructions record to speak with databases. We will consider SQL as an instruction set handed to the database. These directions, often known as SQL language instructions, allow us to carry out a variety of actions. As an illustration, we will use SQL instructions to create a database construction, create a desk or momentary desk, populate the database, retrieve particular data, modify information, and management entry and safety.
Primary SQL Instructions
Right here’s a fast overview of the fundamental SQL instructions defined beneath within the article. Newcomers can study these instructions to know the SQL fundamentals.
- SELECT
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
SQL Assertion
It’s a structured question used to speak with the database. It follows a particular syntax that features clauses, key phrases, and situations to put in writing a question. The customers can customise the SQL statements based mostly on their particular database wants and the operation they’re performing.
Primary SQL Assertion Construction
SELECT column_name;
FROM table_name WHERE situation;Varieties of SQL Instructions
Under are the several types of SQL Instructions:
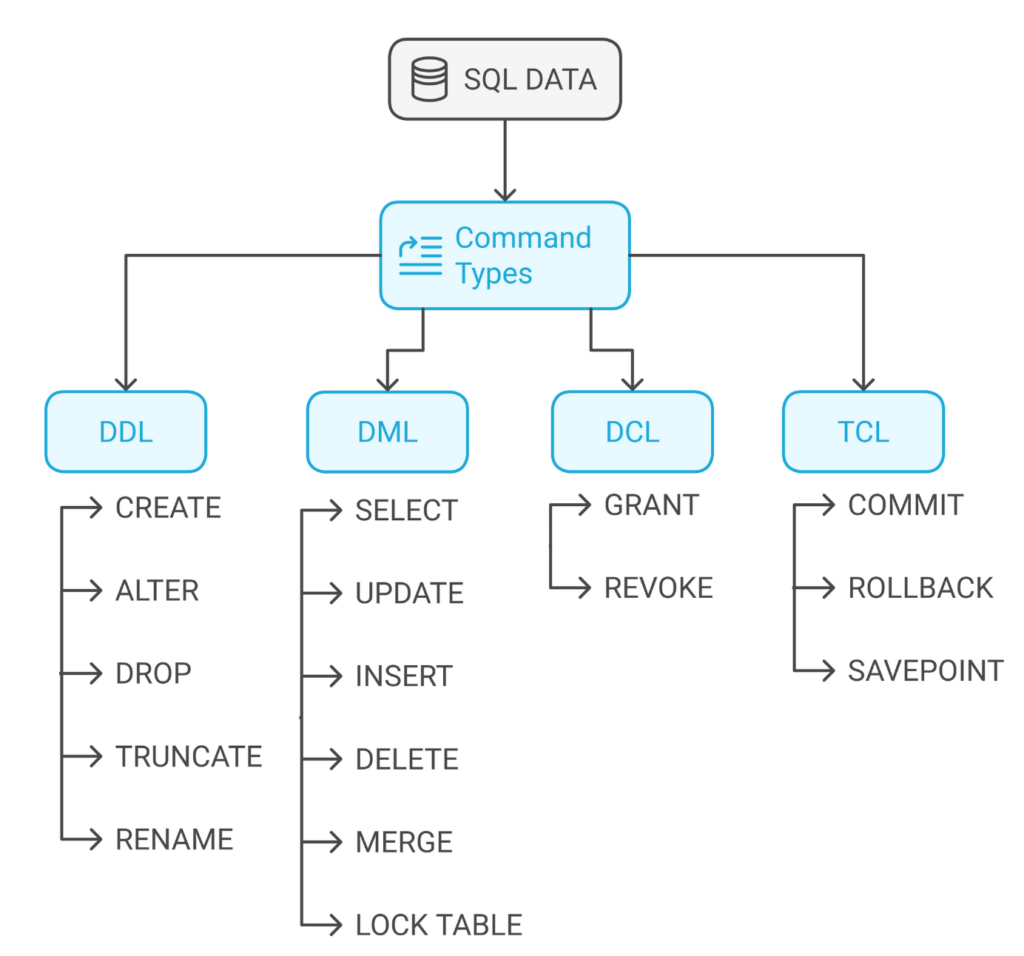
DDL (Knowledge Definition Language) Instructions
DDL consists of database-level instructions to change database buildings. These DDL instructions outline, modify, and delete database tables, views, indexes, and database schemas. Furthermore, the DDL instructions are auto-committed, which ensures that adjustments are completely saved within the database and can’t rolled again to the earlier change.
CREATE
This command creates new database objects. An object could be a Desk or a Database as beneath.
CREATE DATABASE database_db;This SQL assertion creates a brand new database database_db.
CREATE TABLE PERSONS (id INT, identify VARCHAR(255));This SQL assertion creates a brand new desk PERSONS, with columns id and identify.
ALTER
This command modifies the construction of an present object by including, altering, or deleting desk columns, altering information sorts, or renaming objects.
ALTER TABLE PERSONS ADD COLUMN tackle VARCHAR(255);This SQL command provides a brand new column ADDRESS to the PERSONS desk.
DROP
The DROP command deletes present database objects.
DROP DATABASE database_db;This SQL assertion deletes your entire database database_db.
This delete assertion deletes the prevailing desk PERSONS from the database.
TRUNCATE
This deletes all the prevailing information from a desk whereas conserving the unique desk construction. TRUNCATE is often sooner than DELETE because it doesn’t log particular person row deletions.
The above SQL assertion removes all data/rows from the PERSONS desk.
Word: The CASCADE key phrase is required if we’re truncating the desk containing the first keys which can be utilized in different tables as international keys. It is going to truncate all of the dependent tables.
This SQL assertion provides a remark to the definition of a particular database object, which is important for documentation functions.
COMMENT ON TABLE PERSONS IS 'Desk incorporates individuals data';DML (Knowledge Manipulation Language) Instructions
DML consists of SQL fundamental instructions to control the information current within the database. As an illustration, these SQL command lists embody instructions to insert, modify, and delete information. The DML instructions will not be auto-committed, making certain that adjustments will not be completely saved within the database and we will roll again to the earlier state. As an illustration, we will retrieve again the deleted row through the use of the ROLLBACK assertion.
INSERT
This command provides new information to a desk. The beneath command provides a brand new row to the PERSONS desk.
INSERT INTO PERSONS (id, identify) VALUES (10, 'Alice');UPDATE
This updates present information in a desk. As depicted beneath, the UPDATE command updates PERSONS identify with ID 10.
UPDATE PERSONS SET identify = 'Alice' WHERE id = 10;DELETE
This deletes present information based mostly on some situation.
DELETE FROM PERSONS WHERE id = 5;The delete assertion removes the particular person with ID 5 from the PERSONS desk.
DQL (Knowledge Question Language) instructions
DQL command is a subset of SQL instructions particularly designed for querying and retrieving information from the database. DQL command (SELECT) performs particular duties on the information inside schema objects and extracts schema relations based mostly on the question handed to it. It makes use of numerous clauses, features, and key phrases to filter and manipulate the information, thus enhancing its performance.
SELECT (Retrieve Knowledge)
This command retrieves the desired column (identify) from the desk:
SELECT identify FROM PERSONS;To retrieve information from all columns, you should use SELECT * (asterisk):
Nonetheless, utilizing * is often not beneficial because it will increase the quantity of knowledge transferred by together with all columns, even those who aren’t required. This could affect question efficiency. As an alternative, it’s higher to explicitly record the columns you want:
SELECT id, identify, e-mail FROM PERSONS;The SELECT assertion is often used with different clauses and features like DISTINCT, AVG(), WHERE, ORDER BY, GROUP BY, and HAVING to extract information and mixture, filter, kind, or group it to return a number of columns.
DISTINCT
SELECT DISTINCT identify FROM PERSONS;This command ignores the duplicate rows or a number of values and returns solely the distinctive values from the desired column, such because the identify column from the desk PERSONS.
WHERE
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE column_name operator worth;The WHERE clause filters the information based mostly on a specified situation, akin to WHERE identify = ‘Alice’.
AND/OR
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE column_1 = value_1 AND column_2 = value_2;This enables us to mix a number of situations utilizing logical operators.
LIKE
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE column_name LIKE sample;We will use wildcard characters (% for any string, _ for a single character) to carry out a sample search with the LIKE operator.
LIMIT
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name LIMIT quantity;This clause limits the variety of returned rows.
ORDER BY
SELECT column_name FROM table_name ORDER BY column_name ASC | DESC;This clause types the outcomes based mostly on the desired desk column in ascending (ASC) or descending (DESC) order.
GROUP BY
SELECT column_name, COUNT(*) FROM table_name GROUP BY column_name;This clause is usually used with mixture features akin to COUNT() to teams rows based mostly on the values within the specified column..
HAVING
SELECT column_name, COUNT(*) FROM table_name GROUP BY column_name HAVING COUNT(*) > worth;This clause is used with GROUP BY to filter the grouped outcomes.
INNER JOIN
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_1 JOIN table_2 ON table_1.column_name = table_2.column_name;This clause combines rows from a number of tables the place the be part of situation is true.
OUTER JOIN
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_1 LEFT JOIN table_2 ON table_1.column_name = table_2.column_name;This clause retrieves information from two or extra tables. Right here, it combines all rows from the table_1 and matching rows from the table_2. If there’s no match within the table_2, it makes use of NULL values.
AS
SELECT column_name AS 'Alias' FROM table_name;This key phrase shows the outcomes with a short lived column identify.
WITH
WITH temporary_name AS (SELECT FROM table_name) SELECT FROM temporary_name WHERE column_name operator worth;This clause defines a short lived end result set that may be referenced throughout the question.
Combination Capabilities
We will additionally use SELECT statements to extract and mixture information from a database through the use of in-built features akin to AVG(), SUM(), COUNT(), and many others.
AVG()
This operate retrieves the common quantity from the chosen column throughout the SQL assertion. Right here, the AVG() calculates the common worth of the marks column from the scholar desk.
SELECT AVG(MARKS) as AVERAGE_SCORE from STUDENT;SUM()
This operate retrieves the sum of numbers from the chosen column throughout the SQL assertion. Right here, the SUM() calculates the common worth of the marks column from the scholar desk.
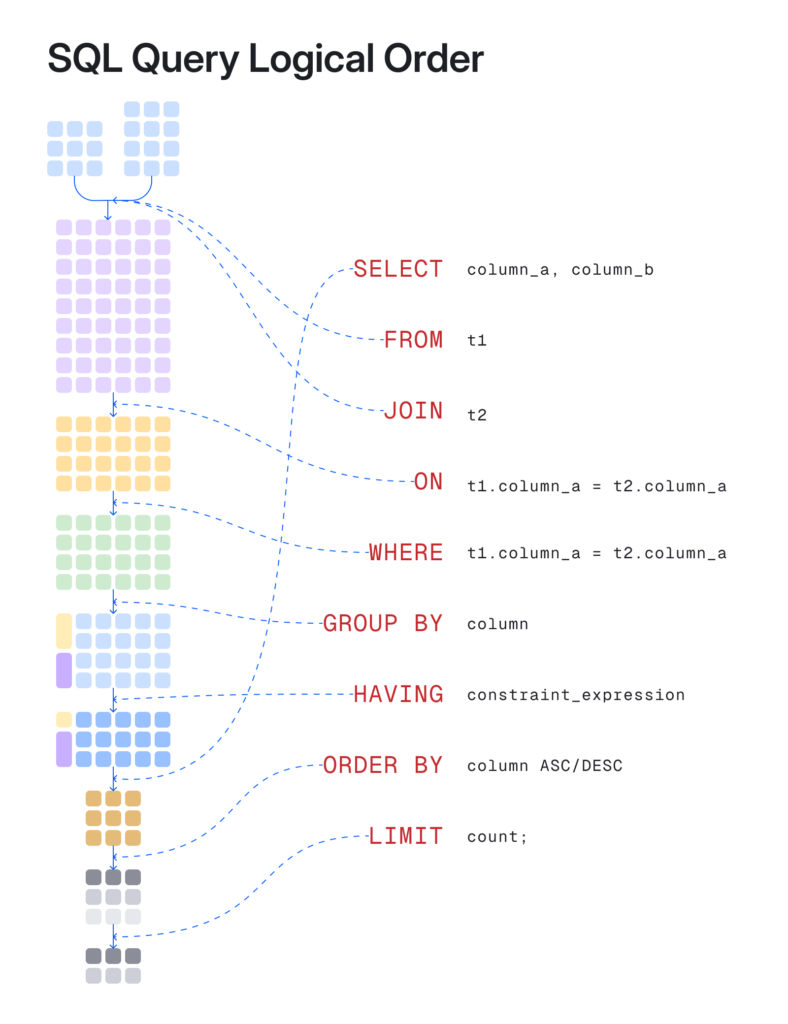
SELECT SUM(MARKS) as TOTAL_MARKS from STUDENT;SQL Question Logical Ordering
Primarily based on the above SQL instructions, there’s a logical order that’s adopted at any time when a desk or set of tables is retrieved. The beneath picture reveals how 2 tables are used to retrieve the relational information based mostly on a number of SQL instructions.
DCL (Knowledge Management Language) instructions
The instructions that handle the rights and permissions of customers in a database belong to DCL. The DCL instructions management entry to the database objects by granting or revoking privileges to customers and in addition management the extent of entry that customers must completely different components of the database.
GRANT
This command is used to grant customers particular privileges to database objects.
GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON PERSONS TO admin; This enables the admin to pick and insert information within the PERSONS desk.
REVOKE
This command is used to revoke assigned privileges from customers.
REVOKE INSERT ON PERSONS FROM admin; This revokes the insert permission on the PERSONS desk from admin.
TCL (Transaction Management Language) instructions
TCL maintains information consistency by making certain that both all statements inside a transaction are efficiently dedicated or none of them are utilized. We use the TCL instructions akin to “COMMIT” and “ROLLBACK” together with the DML instructions(information manipulation language).
COMMIT
This command completely saves all adjustments made inside a transaction.
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
UPDATE accounts SET steadiness = steadiness - 100 WHERE account_id = 123;
UPDATE accounts SET steadiness = steadiness + 100 WHERE account_id = 456;
COMMIT; The commit assertion updates each accounts collectively, making certain that the information is constant. This ensures transactional information is pushed with none discrepancy.
ROLLBACK
This command rolls again all adjustments made inside a transaction because the final COMMIT or ROLLBACK.
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
DELETE FROM accounts WHERE account_id = 555;
ROLLBACK;The above command rolls again the deletion, restoring the accounts.
SAVEPOINT
This command defines a transaction level to which the desk state can rolled again at any given time.
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
UPDATE accounts SET steadiness = steadiness - 100 WHERE account_id = 123;
SAVEPOINT after_insert;
UPDATE accounts SET steadiness = steadiness + 50 WHERE account_id = 123;
ROLLBACK TO after_insert; This rolls again the steadiness addition replace within the accounts after the SAVEPOINT is used.
Conditional Expressions
These expressions add logic to the queries. IF, CASE, and COALESCE statements can be utilized to put in writing conditional expressions.
IF
This command will not be an SQL command however can be utilized in sure SQL dialects akin to MySQL, PostgreSQL, and many others. It executes SQL statements based mostly on a given situation:
IF (Rating > 50) THEN
SELECT 'Cross' AS ExamStatus;
ELSE
SELECT 'Fail' AS ExamStatus;
END IF;
IF Rating > 50 THEN
end result := 'Cross';
ELSE
end result := 'Fail';
END IF;Essential Word: IF statements can’t be utilized in common SQL queries. For conditional logic in customary SQL queries, use the CASE expression as an alternative. CASE is supported by all SQL databases and is taken into account the usual approach to deal with conditional question logic.
CASE
This command works like an if-else assertion within the programming languages:
SELECT StudentID,
CASE
WHEN Rating > 50 THEN 'Cross'
ELSE 'Fail'
END AS ExamStatus
FROM STUDENTS;COALESCE
This SQL operate manages the NULL values and returns the primary non-NULL worth. As an illustration, if I give it a listing of expressions with just one non-NULL worth, it can return solely that worth. Within the beneath code, if the Rating column has a NULL worth, this operate replaces it with zero.
SELECT StudentID,
COALESCE(Score1, 0) AS FinalScore
FROM STUDENTS;Safety Finest Practices
| Follow | Benefit |
| Function-Primarily based Entry Management | Assign consumer roles responsibly based mostly on the consumer’s entry wants |
| Knowledge encryption | Encrypt delicate information akin to passwords and financial institution card particulars |
| Safe Authentication Strategies | Use OAuth 2.0 to get safety towards unauthorized entry |
SQL Dialects
Following are the first SQL dialects and their makes use of on which they’re in contrast and are used for the event functions of varied database methods.
| Dialect | Options |
| PL/pgSQL (PostgreSQL) | – Recognized for superior options akin to JSON/JSONB assist, window features, and CTEs. – Helps full-text search. – Open-source with in depth neighborhood assist. – Helps numerous stacks and used primarily in methods requiring advanced queries with high-performance analytics, akin to monetary methods and information warehousing. |
| MySQL | – Open-source and is broadly used for net growth. – Simple integration with net applied sciences (PHP, Python, and many others.) – Restricted assist for superior analytical options. – Used largely in e-commerce platforms. |
| TSQL (SQL Server) | – Wonderful integration with Microsoft merchandise akin to Azure. – Principally utilized in large-scale purposes. – Offers superior tuning choices. – It may be a pricey possibility, used primarily in ERP methods. |
| PL/SQL (Oracle) | – Designed for high-volume purposes. – Wonderful restoration and concurrency administration. – Excessive prices, and works finest with the Oracle ecosystem. – Utilized in industries requiring excessive availability and scalability. |
SQL Integration
SQL performs a vital function in interacting with relational databases, and its integration with programming languages akin to Python and JAVA and enterprise intelligence (BI) instruments enhances the power to construct highly effective, data-driven purposes.
Suppose there’s a buyer desk within the database and a Python software is being developed that retrieves buyer information and makes use of it to generate buyer insights. Right here is how SQL queries are built-in into Python utilizing SQLite3 or SQLalchemy libraries.
import sqlite3
conn = sqlite3.join('database.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM CUSTOMERS")
rows = cursor.fetchall()Conclusion
All in all, SQL instructions assist us in efficient database administration. The customers can select from its classes and a number of dialects to hook up with the database, carry out operations, and guarantee their information integrity and safety.
FAQs on SQL Instructions
Why ought to we use SQL instructions?
SQL instructions are used to speak the relational databases to retailer, retrieve, and manipulate information.
Can I take advantage of SQL instructions in my purposes?
We will combine SQL utilizing numerous in-built libraries akin to SQLalchemy.
How is the “DELETE” command completely different from the “TRUNCATE” in SQL?
The truncate command deletes all of the desk rows whereas conserving the desk construction intact. Nonetheless, the delete command removes information from a desk based mostly on some consumer’s situation or logic offered within the question. Furthermore, deleted (DML command) objects will be rolled again whereas truncated (DDL command) rows are deleted completely.










