Cloud containers are a scorching matter, particularly in safety. Know-how giants Microsoft, Google and Fb all use them. Google makes use of containers for all the things it runs, totaling a number of billion every week.
The previous decade has seen containers anchoring a rising variety of manufacturing environments. This shift displays the modularization of DevOps, enabling builders to regulate separate options with out affecting all the utility. Containers promise a streamlined, easy-to-deploy and safe technique to implement particular infrastructure necessities and are a light-weight various to VMs.
Let’s look at the evolution of containers and focus on why cloud container safety cannot be neglected.
How do cloud containers work?
Container expertise’s roots have been primarily based on partitioning and chroot course of isolation developed as a part of Linux. Trendy containers are expressed in utility containerization, similar to Docker, and in system containerization, similar to Linux containers (LXC). Each allow IT groups to summary utility code from the underlying infrastructure as they work to simplify model administration and allow portability throughout varied deployment environments.
Containers depend on digital isolation to deploy and run purposes that entry a shared OS kernel with out the necessity for VMs. As a result of they maintain all the mandatory parts — recordsdata, libraries and surroundings variables — containers run desired software program with out worrying about platform compatibility. The host OS constrains the container’s entry to bodily sources, so a single container can’t devour all of a bunch’s bodily sources.
The important thing factor to acknowledge with cloud containers is they’re designed to virtualize a single utility. Contemplate a MySQL container. It supplies a digital occasion of that utility and that’s all it does. Containers create an isolation boundary on the utility stage relatively than on the server stage. If something goes mistaken in that single container — for instance, extreme useful resource consumption by a course of — it solely impacts that particular person container, not the entire VM or entire server. It additionally eliminates compatibility issues between containerized purposes that reside on the identical OS.
Main cloud distributors provide containers as a service, similar to Amazon Elastic Container Service, AWS Fargate, Google Kubernetes Engine, Microsoft Azure Container Cases, Azure Kubernetes Service and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Kubernetes Engine. Containers may also be deployed on public or personal cloud infrastructure with out using devoted merchandise from a cloud vendor.
Containers are deployed in two methods: by creating a picture to run in a container, or by downloading a pre-created picture, similar to these out there on Docker Hub. Docker — initially constructed on LXC — is by far the biggest and hottest container platform. Though alternate options exist, Docker has turn out to be synonymous with containerization.
Cloud container use instances
Enterprises use containers in a wide range of methods to scale back prices and enhance the reliability of software program. Among the many commonest and useful are the next:
- Microservices structure. Containers are perfect for microservices-based utility growth, the place apps are damaged into smaller, independently deployable providers. This improves scalability and simplifies growth cycles. Kubernetes orchestrates the deployment, scaling, and administration of those providers, enabling enterprises to deploy updates with minimal downtime.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud deployments. Containers allow cloud-agnostic portability, letting enterprises run the identical workloads throughout AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform or on-premises with out adjustments to the appliance. This helps catastrophe restoration, value optimization and vendor neutrality methods.
- DevOps and steady integration/steady supply automation. Enterprises use containers in CI/CD pipelines to make sure consistency from growth to manufacturing. Containers allow builders to check in remoted environments that mirror manufacturing, lowering bugs and streamlining integration and deployment workflows.
- Legacy utility modernization. Many enterprises use containers to refactor legacy monolithic purposes into extra agile and maintainable providers. By containerizing older apps, organizations can incrementally modernize their infrastructure with out full rewrites.
- Edge and IoT deployments. Containers might be deployed on the edge to be used instances similar to IoT, manufacturing and retail. Container runtimes similar to K3s (light-weight Kubernetes) assist IT workers help orchestration on the edge with restricted sources.
- Safety and coverage enforcement. By containerizing purposes, enterprises can implement coverage as code utilizing providers like Open Coverage Agent and handle runtime safety by means of integrations with cloud workload safety platforms (CWPPs) and cloud-native utility safety program (CNAPP) instruments.
Cloud containers vs. VMs
In contrast with VMs, container deployments devour solely a minimal quantity of sources. Not like VMs, they do not want a full OS to be put in inside the container, and so they do not want a digital copy of the host server’s {hardware}.
Containers want solely minimal sources to carry out the duty they have been designed for — a couple of items of software program, libraries and the fundamentals of an OS. Consequently, enterprises can deploy two to a few occasions as many containers on a server as VMs, and they are often spun up a lot sooner than VMs.
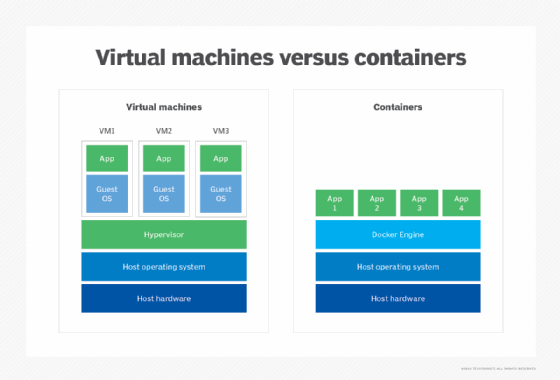
Advantages of containers
Cloud containers are transportable. As soon as a container has been created, it will possibly simply be deployed to completely different servers. From a software program lifecycle perspective, this allows enterprises to rapidly copy containers to create environments for growth, testing, integration and manufacturing. From a software program and safety testing perspective, this ensures the underlying OS is just not inflicting a distinction within the check outcomes.
Containers additionally provide a extra dynamic surroundings. IT can scale up and down extra rapidly primarily based on demand, retaining sources in test.
Challenges of containers
One draw back of containers is the problem of splitting the virtualization into quite a lot of smaller chunks. When there are only a few containers concerned, it is a bonus as a result of the group is aware of precisely what configuration it’s deploying and the place. If, nonetheless, the group totally invests in containers, it is fairly doable to have so many containers that they turn out to be troublesome to handle. Think about deploying patches to lots of of various containers. With out a simple course of, updating a particular library or package deal inside a container picture resulting from a safety vulnerability might be troublesome.
Container administration is usually a continuing headache, even utilizing methods similar to Docker that intention to supply IT with simpler orchestration.
Cloud container safety dangers
Whereas containers provide many benefits, in addition they introduce distinctive safety dangers that enterprises should handle. The ephemeral and dynamic nature of containers calls for a contemporary safety strategy that’s proactive, automated and built-in into DevOps workflows. The next are among the key dangers that organizations ought to prioritize with cloud containers:
- Susceptible photographs. Containers are constructed from photographs, which frequently embody system libraries, runtime dependencies and customized code. Many enterprises use public base photographs from registries similar to Docker Hub, which might comprise unpatched vulnerabilities or malware. Organizations ought to scan photographs constantly, use signed and verified sources, and set up picture allowlists to make sure all builds are safe.
- Container escape. Containers are remoted, however not impenetrable. A container breakout happens when a malicious actor escapes the container runtime to entry the host OS. This threat is elevated if containers run with privileged entry or root permissions. Mitigations embody working containers as non-root customers, utilizing kernel safety modules, similar to AppArmor and SELinux, and deploying sandboxed runtimes, similar to gVisor or Kata Containers. In cloud environments, a few of these mitigation choices is perhaps troublesome or unimaginable resulting from shopper lack of management and configuration.
- Secrets and techniques publicity. Storing credentials, API keys or tokens inside containers or surroundings variables poses vital threat. If compromised, attackers might acquire entry to databases, cloud sources or inside property and providers. Finest practices embody utilizing secret administration instruments, similar to HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets and techniques Supervisor, and avoiding hardcoded secrets and techniques in photographs or Git repositories.
- Provide chain assaults. Containers are a part of a broader software program provide chain that features code, photographs, pipelines, registries and CI/CD tooling. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities on this chain to inject malicious code or compromise deployments. Mitigation requires imposing code signing and picture integrity, utilizing software program payments of supplies the place doable to trace dependencies, and monitoring for anomalies in construct pipelines.
- Runtime threats. As soon as deployed, containers stay susceptible to assaults, together with reverse shells, cryptomining malware and lateral motion in Kubernetes clusters. Safety groups ought to deploy runtime safety instruments — most CNAPP and CWPP platforms prioritize this performance — to watch system calls, container conduct, and community exercise to detect and cease threats in actual time.
- Misconfigured orchestration. Misconfigurations in Kubernetes or different orchestrators are among the many prime container safety dangers. Frequent errors embody exposing Kubernetes dashboards and APIs to the web, working default or weak authentication settings and granting broad cluster roles to service accounts.
- Inadequate community segmentation. Containers typically talk throughout digital networks in a cluster. With out correct community insurance policies, any compromised container might probably facilitate attackers shifting laterally. Implement least privilege utilizing Kubernetes community insurance policies, Calico or service meshes, similar to Istio, to restrict connectivity.
Cloud container safety finest practices
As soon as cloud containers turned widespread, the main focus turned to tips on how to preserve them safe. Contemplate the next:
- Set entry privileges. Docker containers as soon as needed to run as a privileged person on the underlying OS. If key components of the container have been compromised, root or administrator entry might probably be obtained on the underlying OS, or vice versa. As we speak, Docker helps person namespaces, which allow containers to run as particular customers.
- Deploy rootless containers. These containers add an further safety layer as a result of they don’t require root privileges. Subsequently, if a rootless container is compromised, the attacker is not going to acquire root entry. One other good thing about rootless containers is that completely different customers can run containers on the identical endpoint. Docker presently helps rootless containers, however Kubernetes doesn’t.
- Contemplate picture safety. Take note of the safety of photographs downloaded from public repositories, similar to Docker Hub. By downloading a community-developed picture, the safety of a container can’t essentially be assured. Photos might be scanned for vulnerabilities. This step can present some assurance, however its verification processes won’t be thorough sufficient in case you are utilizing containers for notably delicate purposes. On this case, it could be wise to create the picture your self to make sure your safety insurance policies have been enforced and updates are made recurrently. Observe, nonetheless, that company-made photographs are solely as safe as staff make them. Correct coaching for these creating photographs is essential.
- Monitor containers. Deal with containers for delicate manufacturing purposes in the identical method as some other deployment in relation to safety. If a container begins performing oddly or consuming extra sources than crucial, it is simple sufficient to close it down and restart it. It is not fairly a sandbox, however containers present a strategy to preserve untrusted purposes separate and unaware of different purposes on the endpoint.
- Prioritize safety threats and vulnerabilities. Observe container and cloud container safety finest practices and pay attention to container safety vulnerabilities and assaults. Correct deployment and administration are key. Frequently scan containers to make sure photographs and lively containers stay up to date and safe.
- Don’t forget the safety of the server internet hosting the containers. In case your group is utilizing a cloud container supplier, that firm is liable for working, patching and hardening the service.
One remaining level: Though containers are a more recent expertise, this does not imply conventional safety insurance policies and procedures should not be utilized.
Rob Shapland, Ben Cole and Kyle Johnson beforehand contributed to this text.
Dave Shackleford is founder and principal guide at Voodoo Safety, in addition to a SANS analyst, teacher and course creator, and GIAC technical director.










