On this article, you’ll be taught sensible, secure methods to make use of information augmentation to cut back overfitting and enhance generalization throughout photographs, textual content, audio, and tabular datasets.
Subjects we’ll cowl embody:
- How augmentation works and when it helps.
- On-line vs. offline augmentation methods.
- Arms-on examples for photographs (TensorFlow/Keras), textual content (NLTK), audio (librosa), and tabular information (NumPy/Pandas), plus the crucial pitfalls of knowledge leakage.
Alright, let’s get to it.
The Full Information to Information Augmentation for Machine Studying
Picture by Creator
Suppose you’ve constructed your machine studying mannequin, run the experiments, and stared on the outcomes questioning what went unsuitable. Coaching accuracy appears to be like nice, possibly even spectacular, however whenever you verify validation accuracy… not a lot. You’ll be able to clear up this difficulty by getting extra information. However that’s sluggish, costly, and generally simply unimaginable.
It’s not about inventing faux information. It’s about creating new coaching examples by subtly modifying the info you have already got with out altering its which means or label. You’re displaying your mannequin the identical idea in a number of types. You might be instructing what’s vital and what might be ignored. Augmentation helps your mannequin generalize as an alternative of merely memorizing the coaching set. On this article, you’ll find out how information augmentation works in observe and when to make use of it. Particularly, we’ll cowl:
- What information augmentation is and why it helps cut back overfitting
- The distinction between offline and on-line information augmentation
- apply augmentation to picture information with TensorFlow
- Easy and secure augmentation methods for textual content information
- Frequent augmentation strategies for audio and tabular datasets
- Why information leakage throughout augmentation can silently break your mannequin
Offline vs On-line Information Augmentation
Augmentation can occur earlier than coaching or throughout coaching. Offline augmentation expands the dataset as soon as and saves it. On-line augmentation generates new variations each epoch. Deep studying pipelines often favor on-line augmentation as a result of it exposes the mannequin to successfully unbounded variation with out rising storage.
Information Augmentation for Picture Information
Picture information augmentation is essentially the most intuitive place to begin. A canine continues to be a canine if it’s barely rotated, zoomed, or seen below totally different lighting situations. Your mannequin must see these variations throughout coaching. Some widespread picture augmentation methods are:
- Rotation
- Flipping
- Resizing
- Cropping
- Zooming
- Shifting
- Shearing
- Brightness and distinction modifications
These transformations don’t change the label—solely the looks. Let’s reveal with a easy instance utilizing TensorFlow and Keras:
1. Importing Libraries
|
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Dropout from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.picture import ImageDataGenerator from tensorflow.keras.fashions import Sequential |
2. Loading MNIST dataset
|
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# Normalize pixel values X_train = X_train / 255.0 X_test = X_test / 255.0
# Reshape to (samples, top, width, channels) X_train = X_train.reshape(–1, 28, 28, 1) X_test = X_test.reshape(–1, 28, 28, 1)
# One-hot encode labels y_train = to_categorical(y_train, 10) y_test = to_categorical(y_test, 10) |
Output:
|
Downloading information from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/mnist.npz |
3. Defining ImageDataGenerator for augmentation
|
datagen = ImageDataGenerator( rotation_range=15, # rotate photographs by ±15 levels width_shift_range=0.1, # 10% horizontal shift height_shift_range=0.1, # 10% vertical shift zoom_range=0.1, # zoom in/out by 10% shear_range=0.1, # apply shear transformation horizontal_flip=False, # not wanted for digits fill_mode=‘nearest’ # fill lacking pixels after transformations ) |
4. Constructing a Easy CNN Mannequin
|
mannequin = Sequential([ Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation=‘relu’, input_shape=(28, 28, 1)), MaxPooling2D((2, 2)), Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation=‘relu’), MaxPooling2D((2, 2)), Flatten(), Dropout(0.3), Dense(64, activation=‘relu’), Dense(10, activation=‘softmax’) ])
mannequin.compile(optimizer=‘adam’, loss=‘categorical_crossentropy’, metrics=[‘accuracy’]) |
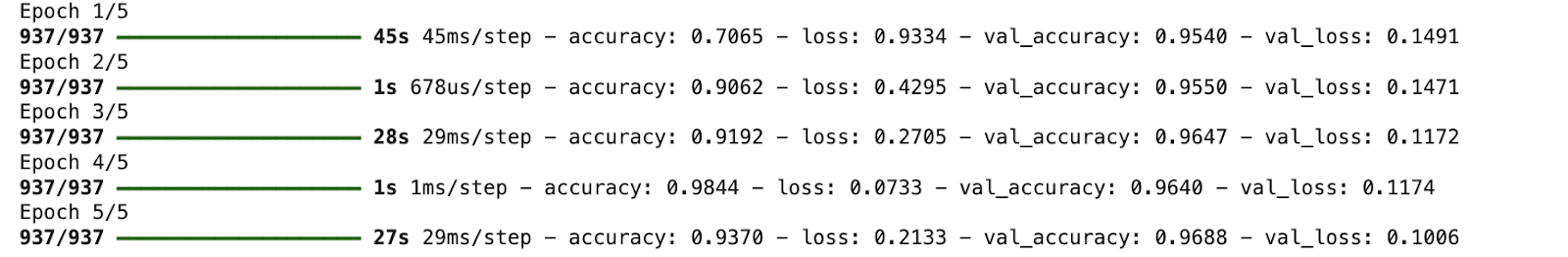
5. Coaching the mannequin
|
batch_size = 64 epochs = 5
historical past = mannequin.match( datagen.movement(X_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True), steps_per_epoch=len(X_train)//batch_size, epochs=epochs, validation_data=(X_test, y_test) ) |
Output:
6. Visualizing Augmented Photos
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Visualize 5 augmented variants of the primary coaching pattern plt.determine(figsize=(10, 2)) for i, batch in enumerate(datagen.movement(X_train[:1], batch_size=1)): plt.subplot(1, 5, i + 1) plt.imshow(batch[0].reshape(28, 28), cmap=‘grey’) plt.axis(‘off’) if i == 4: break plt.present() |
Output:
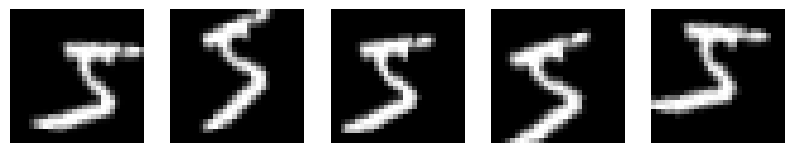
Information Augmentation for Textual Information
Textual content is extra delicate. You’ll be able to’t randomly substitute phrases with out fascinated by which means. However small, managed modifications might help your mannequin generalize. A easy instance utilizing synonym substitute (with NLTK):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
import nltk from nltk.corpus import wordnet import random
nltk.obtain(“wordnet”) nltk.obtain(“omw-1.4”)
def synonym_replacement(sentence): phrases = sentence.break up() if not phrases: return sentence idx = random.randint(0, len(phrases) – 1) synsets = wordnet.synsets(phrases[idx]) if synsets and synsets[0].lemmas(): substitute = synsets[0].lemmas()[0].identify().substitute(“_”, ” “) phrases[idx] = substitute return ” “.be a part of(phrases)
textual content = “The film was actually good” print(synonym_replacement(textual content)) |
Output:
|
[nltk_data] Downloading package deal wordnet to /root/nltk_data... The film was actually good |
Similar which means. New coaching instance. In observe, libraries like nlpaug or back-translation APIs are sometimes used for extra dependable outcomes.
Information Augmentation for Audio Information
Audio information additionally advantages closely from augmentation. Some widespread audio augmentation methods are:
- Including background noise
- Time stretching
- Pitch shifting
- Quantity scaling
One of many easiest and mostly used audio augmentations is including background noise and time stretching. These assist speech and sound fashions carry out higher in noisy, real-world environments. Let’s perceive with a easy instance (utilizing librosa):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
import librosa import numpy as np
# Load built-in trumpet audio from librosa audio_path = librosa.ex(“trumpet”) audio, sr = librosa.load(audio_path, sr=None)
# Add background noise noise = np.random.randn(len(audio)) audio_noisy = audio + 0.005 * noise
# Time stretching audio_stretched = librosa.results.time_stretch(audio, price=1.1)
print(“Pattern price:”, sr) print(“Authentic size:”, len(audio)) print(“Noisy size:”, len(audio_noisy)) print(“Stretched size:”, len(audio_stretched)) |
Output:
|
Downloading file ‘sorohanro_-_solo-trumpet-06.ogg’ from ‘https://librosa.org/information/audio/sorohanro_-_solo-trumpet-06.ogg’ to ‘/root/.cache/librosa’. Pattern price: 22050 Authentic size: 117601 Noisy size: 117601 Stretched size: 106910 |
You must observe that the audio is loaded at 22,050 Hz. Now, including noise doesn’t change its size, so the noisy audio is similar measurement as the unique. Time stretching hurries up the audio whereas preserving content material.
Information Augmentation for Tabular Information
Tabular information is essentially the most delicate information kind to reinforce. In contrast to photographs or audio, you can’t arbitrarily modify values with out breaking the info’s logical construction. Nonetheless, some widespread augmentation methods exist:
- Noise Injection: Add small, random noise to numerical options whereas preserving the general distribution.
- SMOTE: Generates artificial samples for minority courses in classification issues.
- Mixing: Mix rows or columns in a means that maintains label consistency.
- Area-Particular Transformations: Apply logic-based modifications relying on the dataset (e.g., changing currencies, rounding, or normalizing).
- Function Perturbation: Barely alter enter options (e.g., age ± 1 12 months, revenue ± 2%).
Now, let’s perceive with a easy instance utilizing noise injection for numerical options (through NumPy and Pandas):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
import numpy as np import pandas as pd
# Pattern tabular dataset information = { “age”: [25, 30, 35, 40], “revenue”: [40000, 50000, 60000, 70000], “credit_score”: [650, 700, 750, 800] }
df = pd.DataFrame(information)
# Add small Gaussian noise to numerical columns augmented_df = df.copy() noise_factor = 0.02 # 2% noise
for col in augmented_df.columns: noise = np.random.regular(0, noise_factor, measurement=len(df)) augmented_df[col] = augmented_df[col] * (1 + noise)
print(augmented_df) |
Output:
|
age revenue credit score_rating 0 24.399643 41773.983250 651.212014 1 30.343270 50962.007818 696.959347 2 34.363792 58868.638800 757.656837 3 39.147648 69852.508717 780.459666 |
You’ll be able to see that this barely modifies the numerical values however preserves the general information distribution. It additionally helps the mannequin generalize as an alternative of memorizing actual values.
The Hidden Hazard of Information Leakage
This half is non-negotiable. Information augmentation have to be utilized solely to the coaching set. You must by no means increase validation or check information. If augmented information leaks into the analysis, your metrics turn into deceptive. Your mannequin will look nice on paper and fail in manufacturing. Clear separation is just not a finest observe; it’s a requirement.
Conclusion
Information augmentation helps when your information is restricted, overfitting is current, and real-world variation exists. It doesn’t repair incorrect labels, biased information, or poorly outlined options. That’s why understanding your information at all times comes earlier than making use of transformations. It isn’t only a trick for competitions or deep studying demos. It’s a mindset shift. You don’t must chase extra information, however it’s a must to begin asking how your current information may naturally change. Your fashions cease overfitting, begin generalizing, and at last behave the best way you anticipated them to within the first place.










