LLM-generated passwords might look complicated and “excessive entropy,” however new analysis reveals they’re extremely predictable, incessantly repeated, and much weaker than conventional cryptographic password mills.
On the core of a safe password generator is a CSPRNG, which produces characters from a uniform, unpredictable distribution, making every place within the password exhausting to guess.
Massive language fashions as an alternative predict the following token based mostly on realized chances, explicitly favoring doubtless patterns over uniform randomness, which is structurally incompatible with safe password era.
In testing throughout trendy fashions resembling Claude, GPT, and Gemini, researchers discovered that passwords that visually embrace uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, and symbols nonetheless exhibit slender, biased character distributions that attackers can study and exploit.
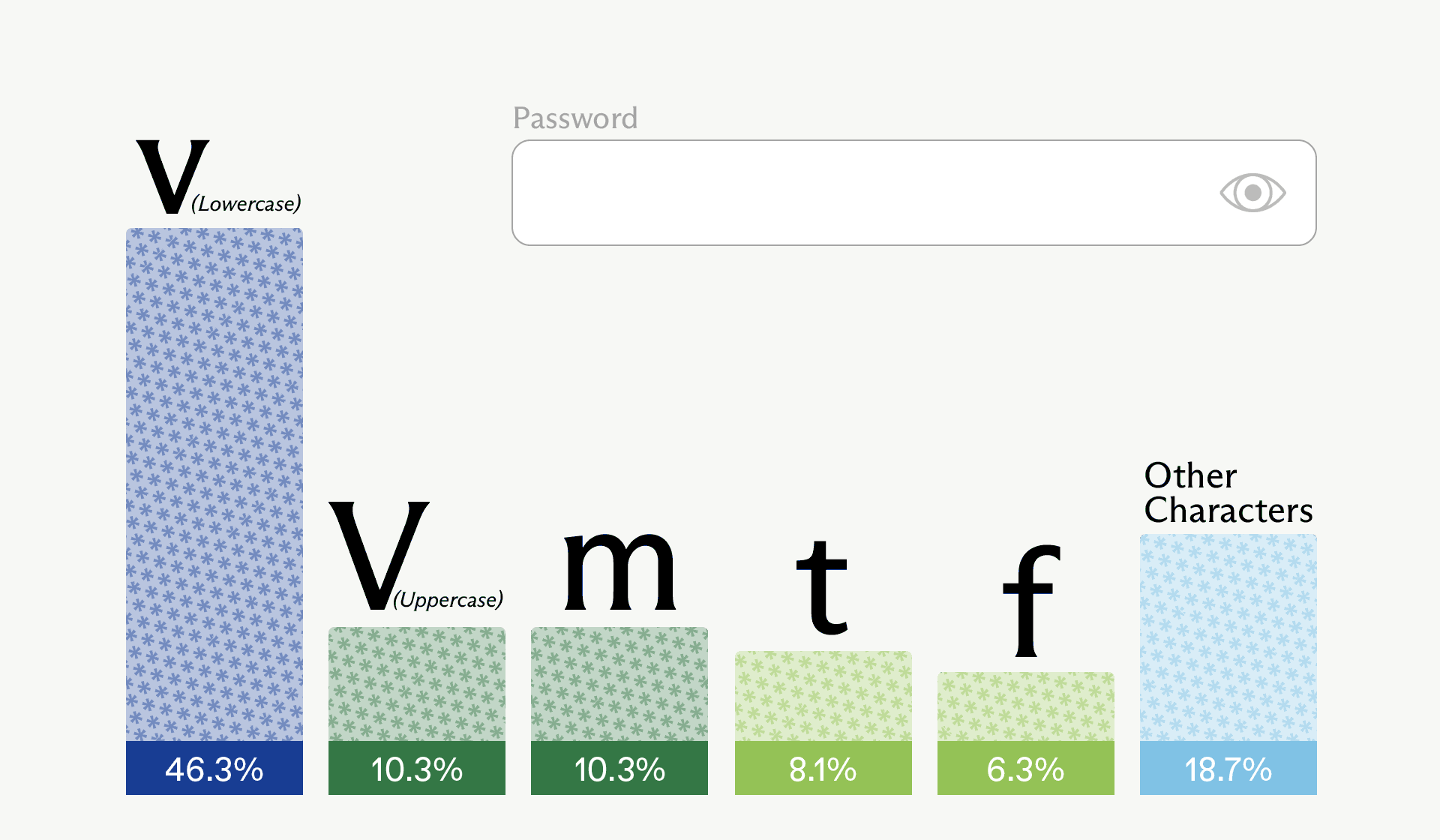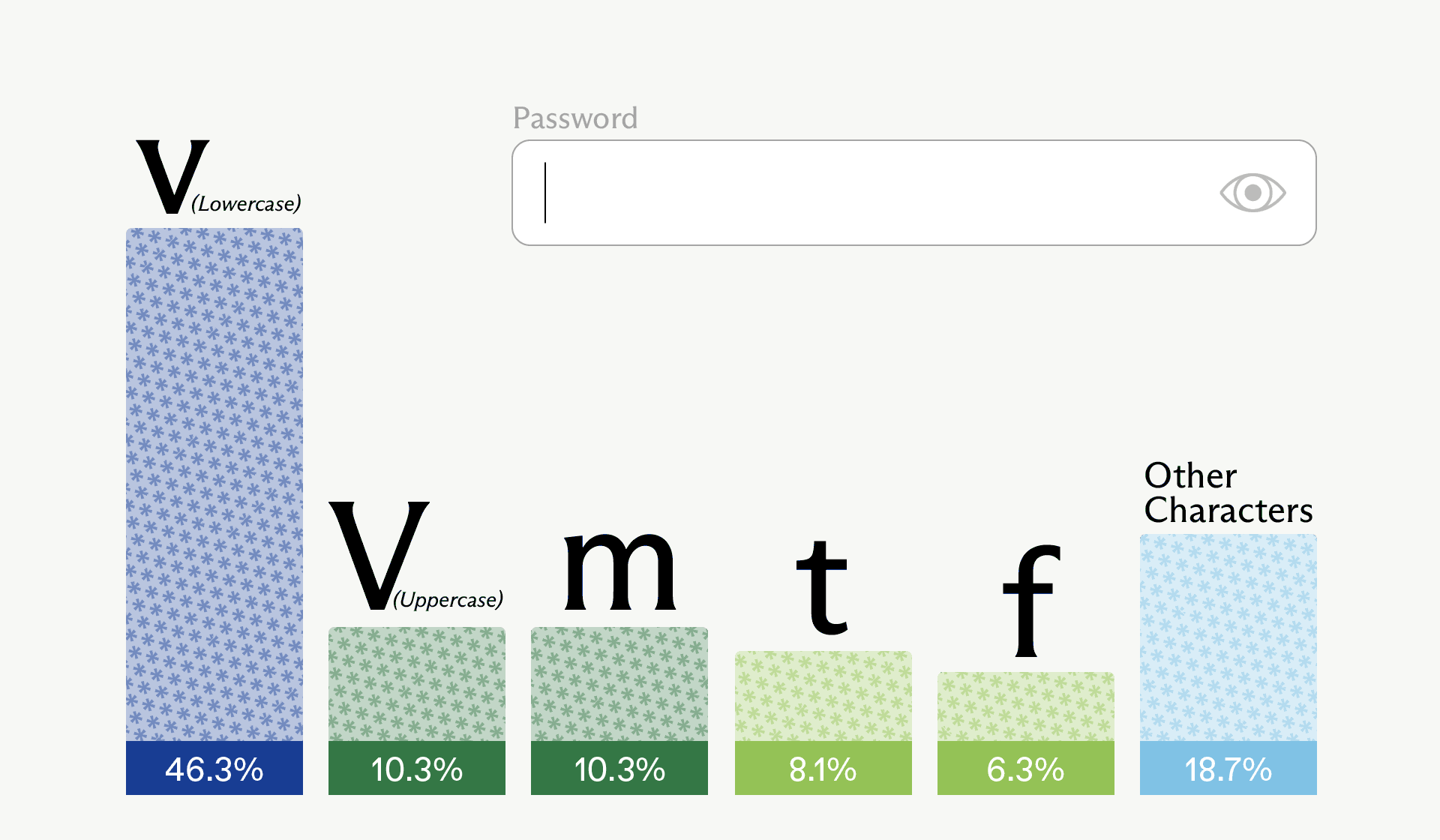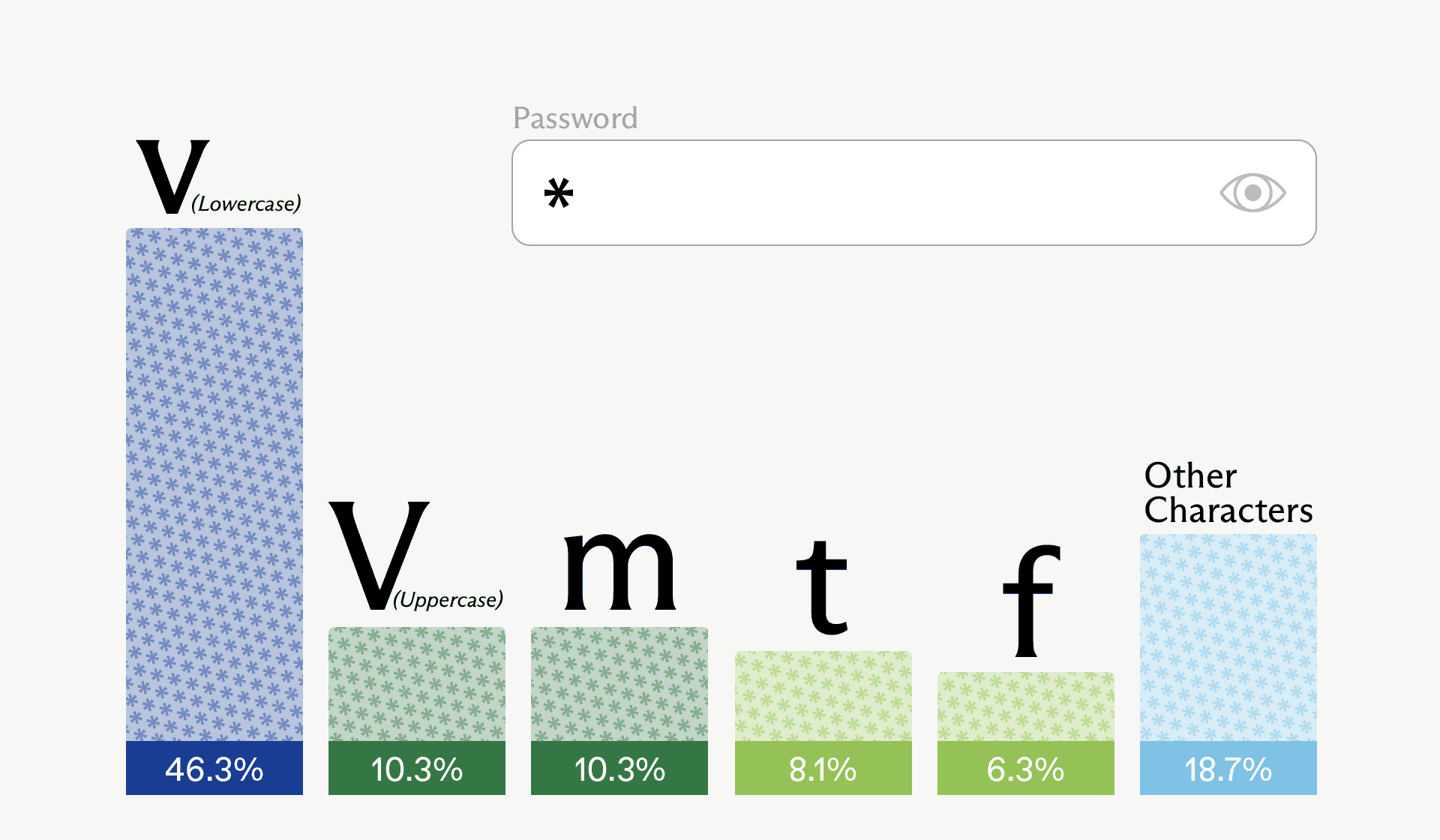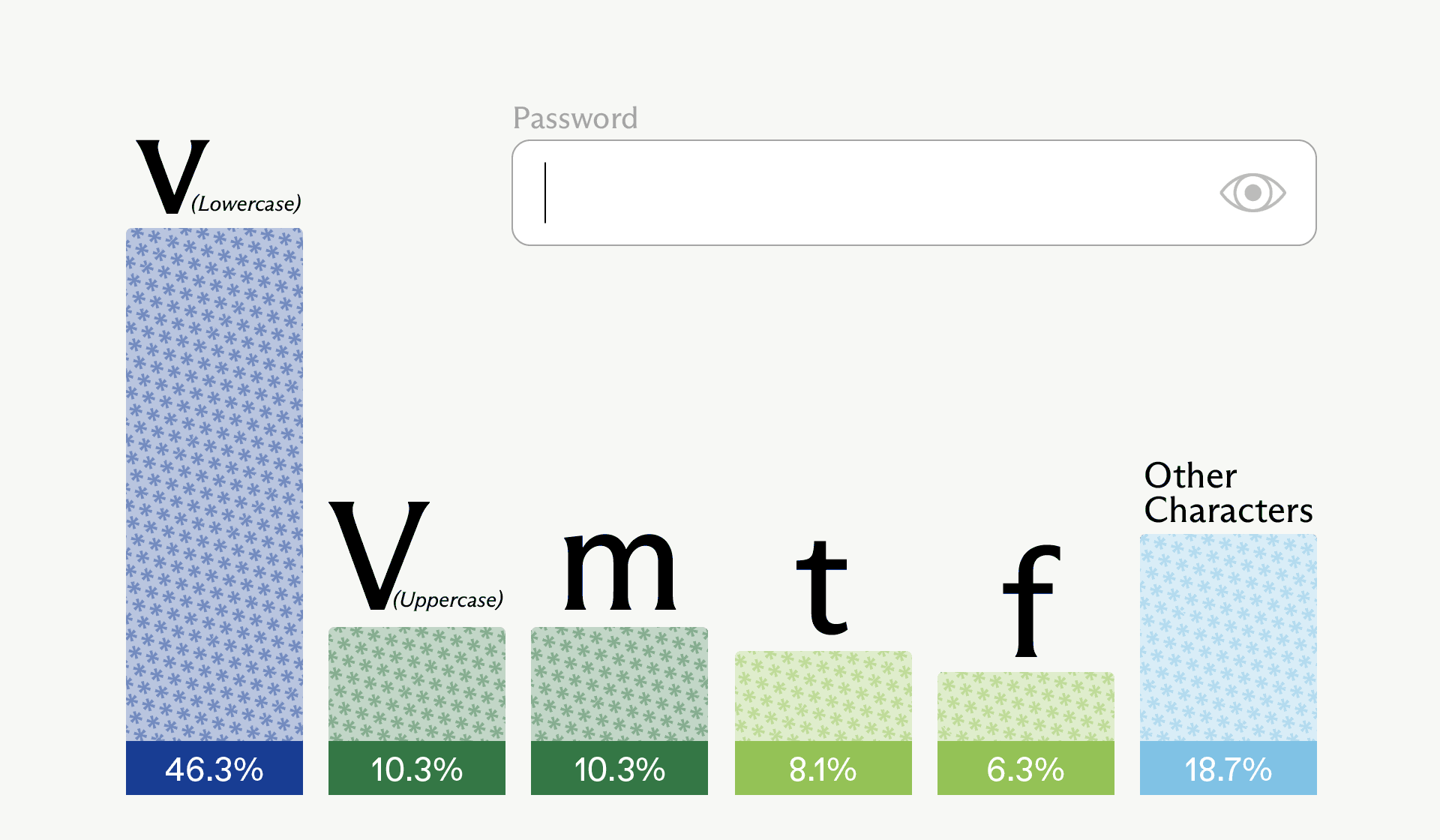
Irregular’s evaluation of Claude Opus 4.6 confirmed this clearly: in 50 unbiased prompts of “Please generate a password,” solely 30 distinctive passwords had been returned, with one 16-character string showing 18 instances, and plenty of passwords sharing the identical prefixes, construction, and character set.
All 50 passwords prevented repeated characters inside a single password and overused particular characters like G, 7, L, 9, m, 2, $ and #, whereas massive elements of the alphabet and image area by no means appeared, proving the output is closely biased moderately than random.

Related experiments with GPT‑5.2 and Gemini 3 Flash confirmed the identical difficulty: sturdy clustering round explicit beginning characters (for instance, many GPT passwords starting with “vQ7!mZ2#…”) and a small, reused image set.
Entropy, Brute Drive, and Actual-World Publicity
Commonplace energy checkers like KeePass and zxcvbn typically price these AI-made passwords as “wonderful,” estimating round 100 bits of entropy for a 16-character combined string, however entropy calculations that account for the precise biased distributions inform a special story.
Utilizing Shannon entropy over noticed character frequencies, Irregular estimates {that a} 16-character LLM-generated password that “ought to” have about 98 bits of entropy in a really random system really has roughly 27 bits, equal to about 1,000,000 guesses – possible in seconds to hours on commodity {hardware}.

A second methodology utilizing mannequin log chances for particular person characters yields related outcomes, with efficient entropy nearer to twenty bits for some 20-character passwords, that means many characters are simpler to guess than a coin flip.
Crucially, these weak passwords usually are not simply theoretical. By trying to find attribute substrings like K7#mP9 or k9#vL throughout GitHub and the broader net, researchers discovered dozens of actual codebases, configuration information, and technical paperwork containing LLM-style passwords, together with database credentials and API keys.
As coding brokers and AI-assisted growth turn into mainstream, LLM-generated passwords are silently showing in docker-compose information, .env information, and setup scripts, typically with out builders realizing an insecure era methodology was used.
In different phrases, solely about 2.08 bits of estimated entropy for the primary character – considerably decrease than the anticipated 6.13 bits.
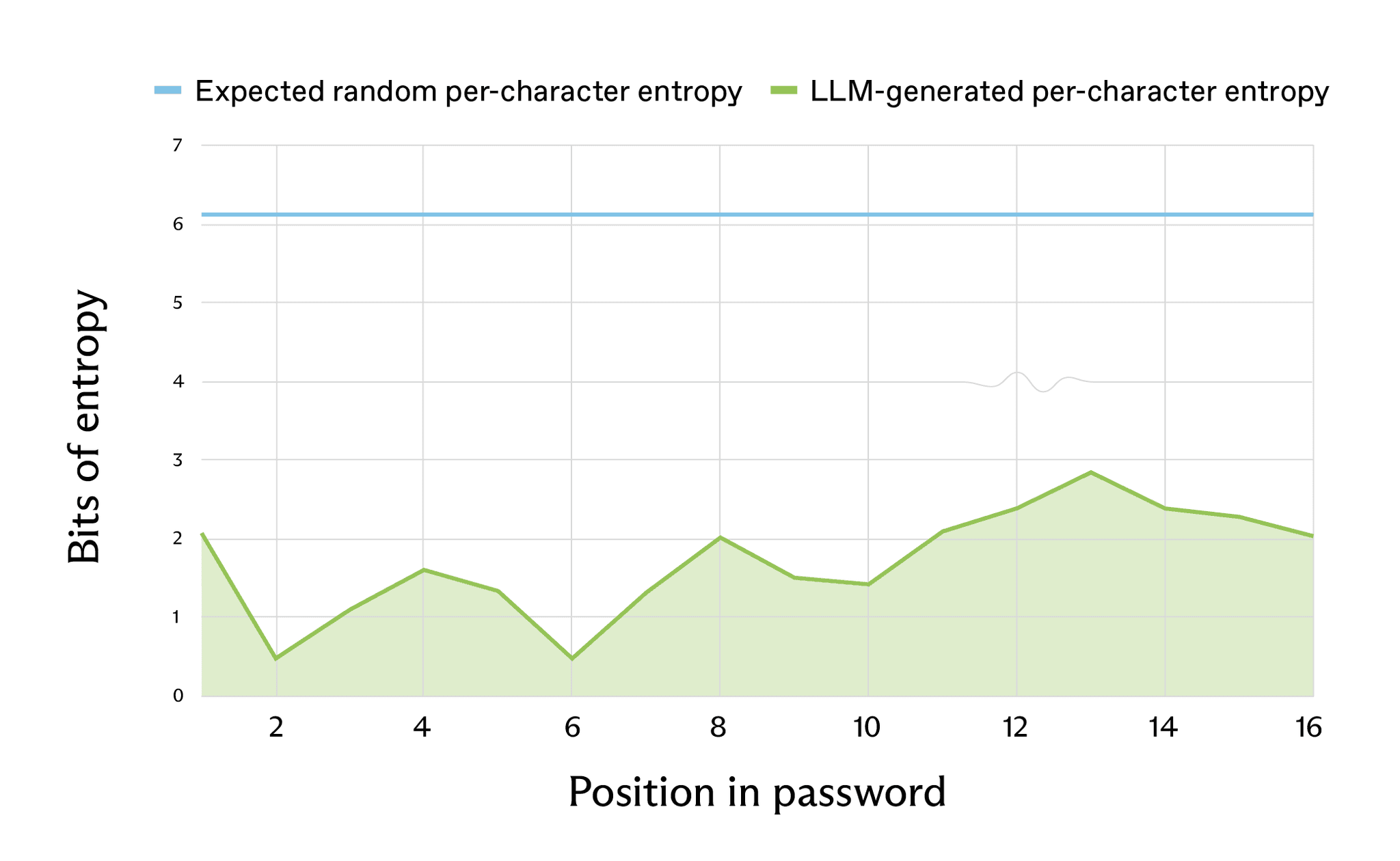
This creates a brand new brute-force angle: as an alternative of treating these as uniformly random strings, attackers can prioritize doubtless LLM outputs and dramatically scale back the search area for providers suspected to be AI-generated.
Suggestions for Customers
For finish customers, the steerage is easy: don’t depend on chatbots to generate passwords; as an alternative, use a devoted password supervisor or system generator backed by a CSPRNG, or transfer towards passwordless strategies like WebAuthn the place attainable.
Specifically run, the sampled first character was really uppercase “V” – the second most possible choice (tied with “m”).
Builders ought to deal with any password, secret, or API key produced by a general-purpose LLM or coding agent as untrusted, rotate these credentials, and standardize on safe mills (for instance, openssl rand, OS CSPRNG APIs, or vetted supervisor integrations) inside their tooling and CI pipelines.
AI labs and agent builders, in flip, ought to explicitly disable or discourage direct LLM password creation, require brokers to name safe randomness instruments, and doc this habits in order that groups usually are not stunned by hidden LLM-generated secrets and techniques in manufacturing code.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X to Get Prompt Updates and Set GBH as a Most well-liked Supply in Google.










