Ajax is a expertise that enables builders to make asynchronous HTTP requests to retrieve or ship knowledge from the server with out the necessity for a full web page refresh. Builders have been utilizing jQuery for a very long time to make this course of much less cumbersome than it might be in pure JavaScript.
In my earlier article An Introduction to jQuery’s Shorthand Ajax Strategies, I mentioned among the mostly used Ajax calls in jQuery, together with $.get(), $.publish(), and $.load(), that are handy strategies for making Ajax requests in jQuery in a couple of traces of code.
However, typically we’d like extra management over the Ajax calls we need to make. For instance, we need to specify what ought to occur in case an Ajax request fails or we have to carry out an Ajax name operate however its result’s solely wanted if retrieved inside a sure period of time. In such conditions, we will depend on one other operate supplied by Ajax in jQuery, referred to as $.ajax(), which is the subject of this tutorial.
Key Takeaways
- Versatility and Management: The jQuery $.ajax() operate provides a versatile and highly effective approach to make asynchronous HTTP requests, permitting builders intensive management over the request and response course of. It helps a wide selection of settings, equivalent to specifying callback features for fulfillment and error, setting request headers, dealing with knowledge varieties, and including authentication tokens for HTTP entry authentication requests, which makes it extremely adaptable to varied situations past the capabilities of shorthand Ajax name features like $.get(), $.publish(), and $.load().
- Complete Configuration Choices: The article highlights the excellent checklist of configuration choices out there with $.ajax(), which may cater to just about any requirement one may need whereas making Ajax calls. From modifying request headers to processing response knowledge, and from dealing with errors to establishing cross-domain requests, $.ajax() gives builders with the instruments essential to fine-tune their Ajax requests and responses to suit their software’s wants exactly.
- Relevance in Trendy Growth: Regardless of the arrival of newer APIs like Fetch, the jQuery $.ajax() operate stays a related and invaluable software in internet improvement, particularly for sustaining legacy codebases or for builders preferring the simplicity and consistency provided by jQuery. Its ease of use, mixed with the depth of performance, ensures that $.ajax() can nonetheless play a vital function in tasks that require Ajax calls, highlighting jQuery’s ongoing utility within the internet improvement ecosystem.
- Superior Error Dealing with and Retry Methods: Sturdy error dealing with is demonstrated utilizing retry mechanisms with exponential backoff, guaranteeing purposes can gracefully get well from non permanent community or server failures. Builders can even outline world error handlers to debug and observe errors throughout a number of requests.
The $.ajax() Operate
The jQuery $.ajax() operate is used to carry out an asynchronous HTTP request. It was added to the library a very long time in the past, present since model 1.0. The $.ajax() operate is what $.get(), $.publish(), and $.load() calls behind the scenes utilizing a preset configuration. The signatures of this operate are proven under:
$.ajax(url[, settings])
$.ajax([settings])The URL in Ajax parameter is a string containing the Ajax URL you need to attain with the jQuery Ajax name, whereas settings is an object literal containing the configuration for the Ajax request.
In its first type, this operate performs an Ajax request utilizing the URL parameter and the choices specified within the settings. Within the second type, the URL is specified within the settings parameter or could be omitted, through which case the request is made to the present web page.
The checklist of the choices accepted by this operate, described within the subsequent part, could be very lengthy, so I’ll preserve their description brief. If you wish to examine their which means in depth, you possibly can check with the official documentation for $.ajax().
The Settings Parameter
There are a number of totally different choices you possibly can specify to bend $.ajax() to your wants. Within the desk under, you’ll find their names and their description sorted in alphabetic order:
| Parameter | Default Worth | Attainable Values | Description and Use Case |
| accepts | { “*”: “*/*” } | Any MIME sort string | The content material sort despatched within the request header that tells the server what sort of response it is going to settle for in return. |
| beforeSend | None | Operate | A pre-request callback operate that can be utilized to change the jqXHR object earlier than it’s despatched. |
| cache | true (aside from script) | true or false | Set this selection to false to drive requested pages to not be cached by the browser. |
| full | None | Operate | A operate to be referred to as when the request finishes (after success and error callbacks are executed). |
| contentType | “software/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8” | MIME sort string | The content material sort of the information despatched to the server. |
| context | window | Any object | An object to make use of because the context (this) of all Ajax-related callbacks. |
| converters | Is determined by dataType | Object mapping | An object containing dataType-to-dataType converters |
| crossDomain | false | true or false | Set this property to true to drive a cross-domain request on the identical area. |
| knowledge | None | Object, String, or Array | The info to ship to the server when performing the Ajax request. |
| dataFilter | None | Operate | A operate for use to deal with the uncooked response knowledge of XMLHttpRequest |
| dataType | textual content | xml, html, json, textual content, and so on. | The kind of knowledge anticipated again from the server. Keep away from utilizing jsonp requests, as it’s largely out of date. |
| error | None | Operate | A operate to be referred to as if the request fails. |
| world | true | true or false | Whether or not to set off world Ajax occasion handlers for this request. |
| headers | None | Object | An object of extra headers to ship to the server. |
| ifModified | false | true or false | Processes the response provided that it has modified for the reason that final request. |
| isLocal | Is determined by surroundings | true or false | Forces jQuery to deal with the present surroundings as native. |
| mimeType | None | MIME sort string | A string that specifies the mime sort to override the XHR mime sort. |
| password | None | String | A password for use with XMLHttpRequest in response to an HTTP entry authentication request. |
| processData | true | true or false | Determines whether or not knowledge must be robotically serialized to a question string. |
| scriptCharset | None | String | Units the charset attribute on the script tag used within the request however solely applies when the “script” transport is used. |
| statusCode | None | Object | Maps HTTP standing codes to callback features. |
| success | None | Operate | A operate to be referred to as if the request succeeds. |
| timeout | 0 (no timeout) | Integer | A quantity that specifies a timeout (in milliseconds) for the request. |
| sort | “GET” | “GET”, “POST”, and so on. | The kind of request to make. |
| url | Present web page URL | String | A string containing the URL to which the request is shipped. |
| username | None | String | A username for use with XMLHttpRequest in response to an HTTP entry authentication request. |
| xhr | None | Operate | A callback operate for creating the XMLHttpRequest object. |
| xhrFields | None | Object | An object to set on the native XHR object. |
That’s a reasonably lengthy checklist, isn’t it? Effectively, as a developer, you in all probability stopped studying this checklist on the fifth or sixth factor, I assume, however that’s positive. The following part will likely be extra thrilling as a result of we’ll put the $.ajax() operate and a few of these choices into motion.
Placing It All Collectively
On this part, we’ll focus on $.ajax() operate intimately and a few of its choices in motion.
A First Instance of $.ajax()
We’ll begin with a easy demo that reproduces the identical code we developed in the earlier article. As a recap, we’ll think about that we’ve a component in our web site having an ID of foremost that represents the principle content material. What we need to do is asynchronously load knowledge from the principle content material of the pages referenced by the hyperlinks in the principle menu, which ideally has foremost menu as its ID. We need to retrieve solely the content material inside this factor as a result of the opposite components of the format don’t change, in order that they don’t must be loaded.
This method is meant as an enhancement as a result of if the consumer visiting the web site has JavaScript disabled, they may have the fallback of nonetheless having the ability to browse the web site utilizing the same old synchronous mechanism. On this instance, we’re assuming that every one the hyperlinks within the menu are inside hyperlinks.
We’ll begin with a easy demo that reproduces the identical code we developed within the earlier article, however this time we’ll undertake $.ajax(). The code we developed beforehand is proven under to your comfort:
$('#main-menu a').on('click on', operate(occasion) {
occasion.preventDefault();
$('#foremost').load(this.href + ' #foremost *', operate(responseText, standing) {
if (standing === 'success') {
$('#notification-bar').textual content('The web page has been efficiently loaded');
} else {
$('#notification-bar').textual content('An error occurred');
}
});
});Updating this snippet to make use of the $.ajax() operate, we receive the code proven under:
$('#main-menu a').on('click on', operate(occasion) {
occasion.preventDefault();
$.ajax(this.href, {
success: operate(knowledge) {
$('#foremost').html($(knowledge).discover('#foremost *'));
$('#notification-bar').textual content('The web page has been efficiently loaded');
},
error: operate() {
$('#notification-bar').textual content('An error occurred');
}
});
});Right here you possibly can see that I used the primary type of the operate. I’ve specified the URL to ship the request to as the primary parameter after which a settings object because the second parameter. The latter takes benefit of simply two of the a number of properties mentioned within the earlier part — success and error — to specify what to do in case of request succeeds or a request fails respectively.
Including Customized Headers and Dealing with HTTP Entry Authentication Requests
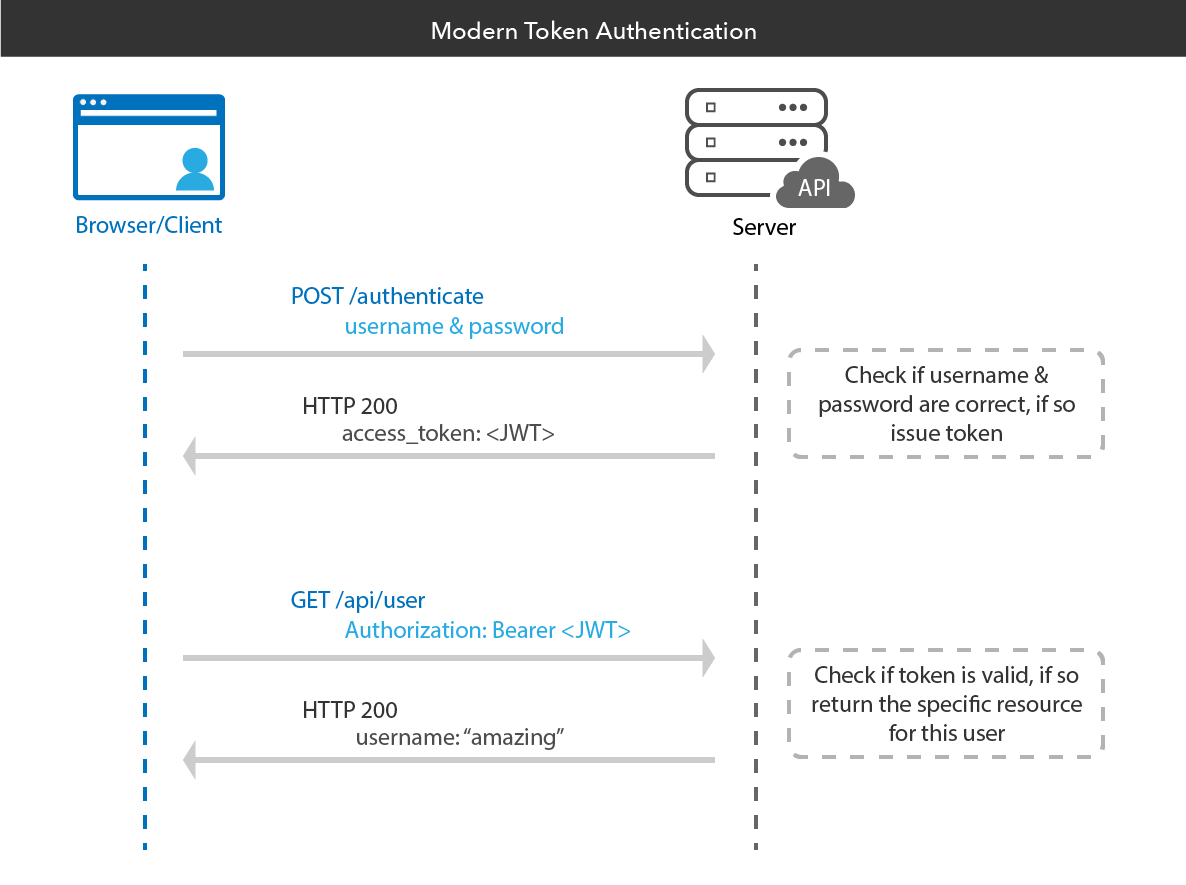
Picture Supply: https://developer.okta.com/weblog/2019/02/14/modern-token-authentication-in-node-with-express
On this second instance, we’ll discover easy methods to improve your AJAX requests by including customized headers, dealing with authentication tokens, and interacting with APIs that require particular safety measures. These are frequent situations when working with fashionable internet purposes that talk with exterior APIs.
Let’s say you’re interacting with an API that requires a token for an HTTP entry authentication request. You may embody this token as a part of the request headers utilizing the headers possibility in $.ajax():
$('#main-menu a').on('click on', operate(occasion) {
occasion.preventDefault();
$.ajax({
url: this.href,
headers: {
"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_TOKEN_HERE",
"X-Customized-Header": "CustomValue"
},
success: operate(knowledge) {
$('#foremost').html($(knowledge).discover('#foremost *'));
$('#notification-bar').textual content('The web page has been efficiently loaded with customized headers');
},
error: operate() {
$('#notification-bar').textual content('An error occurred whereas loading the web page with customized headers');
}
});
});On this instance, the Authorization header features a bearer token, which is often used to authenticate the request with an API securely. Moreover, the X-Customized-Header serves as an additional metadata header, typically required by proprietary APIs to offer extra context or adjust to particular server necessities.
Including customized headers is especially helpful when working with safe APIs, guaranteeing correct authentication and offering the server with any mandatory contextual info.
Managing Advanced Information Constructions with $.ajax()
APIs typically require structured knowledge, equivalent to nested JSON objects, to deal with filters or hierarchical info. The next instance demonstrates easy methods to ship structured knowledge utilizing the information property of $.ajax() operate:
$.ajax({
url: '/api/merchandise',
headers: {
"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_TOKEN_HERE",
"X-Customized-Header": "CustomValue"
},
sort: 'POST',
contentType: 'software/json',
knowledge: JSON.stringify({
class: 'electronics',
filters: {
model: 'Samsung',
priceRange: [100, 500]
}
}),
success: operate(knowledge) {
$('#foremost').html($(knowledge).discover('#foremost *'));
$('#notification-bar').textual content('Thed ata has been despatched efficiently');
},
error: operate() {
$('#notification-bar').textual content('An error occurred whereas sending knowledge');
}
});
Right here, the contentType: ‘software/json’ specifies the information format being despatched, and JSON.stringify() converts JavaScript objects into JSON strings for compatibility with APIs. That is very best for APIs requiring advanced queries or hierarchical filters.
Actual-World Utility Situation: Dwell Search Function
Now that you simply perceive how $.ajax() works, let’s check out a real-life situation through which $.ajax() is extremely helpful. For instance, think about you’re constructing a web-based retailer, and also you need customers to seek for merchandise dynamically as they sort in a search field. As an alternative of reloading the whole web page each time, the search outcomes ought to seem immediately, giving customers a clean and interactive expertise.
How It Works
When a consumer varieties within the search field, their question string is shipped to the server by way of an AJAX request. The server processes the question string and returns matching merchandise, that are displayed instantly on the web page. This retains the expertise quick and seamless.
Right here’s how one can deal with it:
$('#search-box').on('enter', operate() {
let question = $(this).val().trim();
if (question.size > 2) {
$.ajax({
url: "/search-products",
sort: "GET",
knowledge: { question: question },
success: operate(response) {
let outcomes = response.merchandise.map(product => `
${product.identify}
${product.description}
Value: $${product.worth}
`).be part of('');
$('#search-results').html(outcomes);
},
error: operate() {
$('#search-results').html('Unable to load outcomes. Please strive once more.
');
}
});
} else {
$('#search-results').empty();
}
});Why This Issues
Take into consideration how a lot time customers save once they don’t must reload the web page to see search outcomes. This method:
- Enhances Usability: Outcomes seem in real-time, making the interface really feel extra responsive.
- Saves Bandwidth: Solely the required knowledge is fetched, decreasing pointless load on the server.
- Improves Consumer Expertise: A quicker, smoother interplay retains customers engaged.
By making use of this easy sample, you possibly can remodel a fundamental search field right into a dynamic, user-friendly characteristic that elevates your internet software.
Finest Practices for Safe and Dependable AJAX Requests
To make sure your AJAX requests are safe and dependable, it’s necessary to observe finest practices that tackle frequent safety considerations and optimize the event course of.
Error Dealing with Methods
- Implement strong error dealing with utilizing an error callback operate or world handlers to offer significant suggestions to customers and deal with retries gracefully.
- Keep away from infinite retries to forestall server overload; as a substitute, implement methods like exponential backoff.
Cross-Area Requests and Safety Concerns
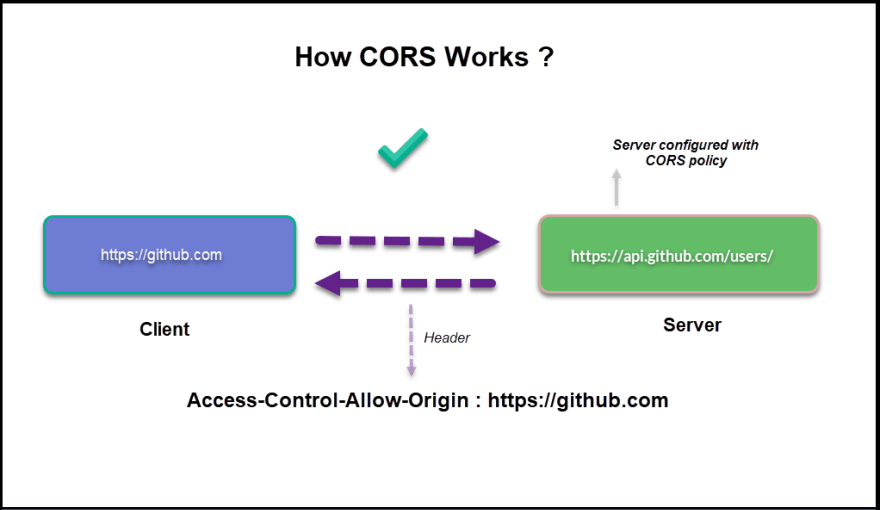
Picture Supply: https://medium.com/swlh/how-cors-cross-origin-resource-sharing-works-79f959a84f0e
- Use Cross-Origin Useful resource Sharing (CORS) to deal with cross-domain requests securely. Make sure the server explicitly permits requests from trusted origins.
- Forestall Cross-Website Scripting (XSS) assaults by escaping or sanitizing inputs and outputs. Use instruments like DOMPurify to sanitize consumer inputs earlier than processing them.
- Validate all consumer inputs on each the consumer and server sides to make sure that solely anticipated knowledge is processed.
- At all times transmit delicate knowledge over HTTPS to safe knowledge in transit and forestall eavesdropping or man-in-the-middle assaults.
Enhance AJAX Safety
- Use libraries like DOMPurify to sanitize consumer inputs and forestall XSS assaults.
let cleanInput = DOMPurify.sanitize(userInput); - Use HTTP headers like Content material-Safety-Coverage (CSP) to mitigate injection assaults.
- Implement anti-CSRF tokens to forestall Cross-Website Request Forgery assaults.
$.ajax({ url: '/secure-endpoint', sort: 'POST', headers: { 'X-CSRF-Token': csrfToken }, knowledge: { enter: cleanInput } }); - Keep away from exposing delicate API keys within the front-end by storing them securely on the server aspect.
- Repeatedly audit and replace your dependencies, together with jQuery, to handle identified vulnerabilities.
Debugging Ajax Requests: What To Do When a Request Fails
Debugging Ajax jQuery requests can typically be tough as a consequence of their asynchronous nature and the involvement of each client-side and server-side code. Listed here are some efficient suggestions for debugging points associated to the jQuery $.ajax() technique:
1. Use Browser Developer Instruments
- Community Tab: Verify the Community tab in your browser’s developer instruments to examine the Ajax request. Confirm the request URL, headers, payload, and response. Search for any errors or surprising standing codes.
- Console Tab: Search for JavaScript errors or warnings within the Console tab that may point out issues together with your jQuery Ajax name or its callback features.
2. Verify the Server-Aspect Logs
- If the jQuery Ajax name reaches the server however doesn’t behave as anticipated, verify the server-side logs for errors or warnings. This could present clues about points within the server-side code or configuration.
3. Log Request and Response
- Quickly add console.log() statements within the success, error, and full callbacks of the $.ajax() name to log the response or any error messages. This can assist you perceive what the server is returning or why the request is perhaps failing.
4. Confirm the Information Sort
- Be certain that the dataType possibility in your $.ajax() name matches the precise sort of information returned by the server. Mismatches right here could cause jQuery to incorrectly course of the response, resulting in surprising habits.
5. Check API Endpoints Individually
- Use instruments like Postman or curl to manually check the API endpoint. This can assist you confirm that the API is working accurately and perceive the anticipated request format and response knowledge.
6. Validate JSON Responses
- For JSON knowledge, validate the response utilizing a web-based JSON validator or debugging instruments to make sure it’s well-formed. Malformed JSON could cause parsing errors.
7. Use jQuery.ajaxError() for International Error Dealing with
- Bind an occasion handler to ajaxError on the doc to catch and deal with Ajax request errors globally. This can assist you determine and debug Ajax requests that fail throughout your software.
$(doc).ajaxError(operate(occasion, jqxhr, settings, thrownError) {
console.error("AJAX Request Failed: ", settings.url, thrownError);
});8. Simplify and Isolate
- Simplify your $.ajax() name or isolate it in a easy surroundings/web page to confirm its habits with out interference from different scripts or Ajax calls.
Typically, these errors could be non permanent as a consequence of community points. Implementing retries with rising delays (exponential backoff) can robotically deal with such conditions and enhance the reliability of your software.
operate ajaxWithRetry(url, retries, delay) {
$.ajax({
url: url,
success: operate(knowledge) {
console.log('Success:', knowledge);
},
error: operate() {
if (retries > 0) {
setTimeout(() => {
ajaxWithRetry(url, retries - 1, delay * 2);
}, delay);
} else {
console.error('Failed after retries');
}
}
});
}
ajaxWithRetry('/fetch-data', 3, 1000);The operate retries the request as much as 3 instances, doubling the delay after every failure. This helps to deal with community glitches or non permanent server unavailability.
Optimizing the Efficiency of Ajax Requests
Optimizing the efficiency of Ajax requests is essential for creating quick and responsive internet purposes. When utilizing the jQuery $.ajax() operate, contemplate the next tricks to improve efficiency:
1. Use GET for Retrieving Information
- HTTP GET requests are typically quicker and could be cached by the browser. Use HTTP GET to retrieve knowledge each time potential and reserve HTTP POST requests for actions that change the server’s state.
2. Restrict Information Switch
- Reduce Payload Dimension: Ship and obtain solely the information that’s mandatory. Massive payloads can considerably decelerate your software.
- Compress Information: Use compression strategies for each request and uncooked response knowledge in case your server and shoppers assist it.
3. Cache Responses
- Browser Caching: Use HTTP headers equivalent to Cache-Management and ETag to allow the browser to cache incessantly requested sources.
Cache-Management: max-age=3600
- Utility-Degree Caching: Cache knowledge regionally utilizing instruments like localStorage, sessionStorage, IndexedDB, or fashionable libraries equivalent to Dexie.js, and PouchDB for incessantly accessed sources.
let cachedData = localStorage.getItem("merchandise"); if (cachedData) { renderProducts(JSON.parse(cachedData)); // Use cached knowledge } else { $.ajax({ url: "/api/merchandise", sort: "GET", success: operate(knowledge) { localStorage.setItem("merchandise", JSON.stringify(knowledge)); // Cache knowledge renderProducts(knowledge); } }); } - Server-Aspect Caching: Instruments like Redis or Memcached can cache knowledge on the server, decreasing database queries for incessantly requested knowledge.
4. Asynchronous Requests
- Be certain that your requests are asynchronous (async: true, which is the default) to forestall blocking the principle thread. This retains your software responsive whereas the information is being fetched.
5. Batch Requests
- Cut back HTTP Requests: Mix a number of requests right into a single one if you happen to’re fetching knowledge from the identical endpoint, decreasing the overhead of a number of HTTP connections.
6. Use Promise Chains for A number of Requests
- When you have dependent requests, use jQuery’s promise and .then() chaining to deal with them in a clear and environment friendly means, decreasing callback nesting and enhancing readability.
7. Error Dealing with
- Implement strong error dealing with to cope with failed requests. Keep away from pointless retries for requests which can be prone to fail repeatedly.
8. Timeout Configuration
- Set an affordable timeout to your AJAX requests (timeout setting). This prevents requests from hanging indefinitely and degrading the consumer expertise.
9. Keep away from Pointless Ajax Calls
- Earlier than making a request, verify if the information is already out there on the consumer aspect or if the operation is absolutely mandatory.
10. Optimize Server-Aspect Processing
- Be certain that the server-side processing of Ajax requests is optimized. Quicker server responses result in higher efficiency.
11. Reduce DOM Manipulations
- When updating the DOM based mostly on Ajax responses, decrease the variety of manipulations and reflows. Use doc fragments or batch updates to the DOM.
Options to jQuery’s $.ajax()
With fashionable JavaScript, there are quite a few choices for making HTTP requests, every catering to totally different wants. Whereas $.ajax() has been a dependable selection for years, newer alternate options like Fetch API have gained recognition for contemporary improvement. Let’s examine these choices.
When To Use $.ajax()
- Best for legacy tasks already utilizing jQuery.
- Handy for fast integration in environments the place jQuery is already loaded.
- Offers built-in assist for advanced configurations and callbacks.
When To Use Fetch or Different Options
- Really helpful for fashionable purposes or frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular.
- Gives cleaner syntax with Guarantees and async/await.
- Extra light-weight, with no dependency on exterior libraries.
- Supported natively in JavaScript and fashionable browsers.
Different alternate options to $.ajax() embody fashionable instruments like Axios, SuperAgent, and Node-Fetch, every catering to particular wants in fashionable improvement.
Model Compatibility and Deprecation Notices
As jQuery has developed, some options and practices within the $.ajax() API have been deprecated or changed with fashionable alternate options. Staying conscious of those adjustments ensures compatibility and maintainability in your tasks.
- Synchronous Requests (async: false)Using synchronous requests is deprecated as a consequence of their impression on consumer expertise. At all times use asynchronous requests (async: true), which is the default.
- JSONP Request AssistJSONP requests had been as soon as used for cross-domain requests and are actually largely out of date. Use fashionable strategies like CORS for safe cross-domain communication.
- Deprecated ChoicesStrategies like jqXHR.error() and jqXHR.success() are changed by completed() and fail() for promise-based dealing with:
$.ajax("/api/knowledge") .completed(response => console.log("Success:", response)) .fail(error => console.error("Error:", error)); - Shift Towards Trendy OptionsNative instruments just like the Fetch API or libraries like Axios are sometimes most well-liked in fashionable tasks as a consequence of their simplicity and compatibility with async/await.
Conclusion
On this tutorial, I mentioned essentially the most highly effective of the Ajax features provided by jQuery, $.ajax(). It lets you carry out Ajax requests with a number of management over how the request is shipped to the server and the way the response is processed. Because of this operate, you might have the instruments you might want to fulfill your entire undertaking’s necessities in case not one of the shorthand features is an effective match.
To have an excellent higher understanding of the potential of this operate, I encourage you to play with the corresponding code samples and to attempt to modify the code to make use of another choices accepted by the settings parameter.
If you wish to be taught extra about JavaScript, try our JavaScript titles at SitePoint Premium. Have enjoyable!
FAQs About jQuery’s Ajax Operate
What Is jQuery’s Ajax Operate?
jQuery Ajax operate is a strong and versatile technique that lets you make asynchronous HTTP requests from an internet web page to a server and deal with the response with out having to reload the whole web page. It helps superior configurations like customized headers, authentication tokens, and file uploads.
How Do I Use jQuery’s Ajax Operate?
To make use of the jQuery Ajax operate, you might want to name $.ajax() and supply it with a configuration object that specifies varied settings just like the URL, HTTP technique, knowledge to ship, and callbacks to deal with the response. You may also outline safety headers and deal with errors gracefully with retry mechanisms if wanted.
How Does an Ajax Name jQuery Work?
An Ajax name jQuery is carried out utilizing the $.ajax() technique. This technique permits builders to make asynchronous HTTP requests to retrieve or ship knowledge to a server with out refreshing the web page.
What Are the Primary Parameters of the $.ajax() Operate?
The essential parameters of the $.ajax() operate embody:
- url: The goal URL for the request.
- technique: HTTP POST request or GET request.
- knowledge: The info to be despatched with the request, both as JSON, question strings, or type knowledge.
- success: A callback operate to deal with a profitable response.
- error: A callback operate to handle errors.
What Is the Goal of the Success Callback in $.ajax()?
The success callback is executed when the Ajax request succeeds. It receives the uncooked response knowledge returned from the server as its parameter, permitting you to course of and manipulate the information as wanted. For instance, dynamic search outcomes could be up to date immediately utilizing this callback.
Can I Deal with Errors in jQuery Ajax Requests?
Sure, you possibly can. The error callback operate within the Ajax request jQuery configuration permits you to outline a operate to deal with errors that happen through the Ajax request. This may be helpful for situations like community errors or server-side points.
How Can I Ship Information Together with My Ajax Request?
You should use the information parameter within the $.ajax() configuration to ship knowledge to the server. This knowledge could be in varied codecs like a question string, a JSON object, or serialized type knowledge.
Is the jQuery Ajax Operate the Solely Technique to Make Ajax Requests?
No. Trendy alternate options, just like the Fetch API, Axios, SuperAgent, and Node-Fetch, present easier syntax and higher assist for Guarantees and async/await. The article features a detailed comparability that will help you select the suitable software to your undertaking based mostly on its necessities.
Is jQuery Required for Utilizing Ajax in Net Growth?
No. Trendy browsers natively assist the Fetch API, which may substitute jQuery’s Ajax operate for many use instances. Nonetheless, jQuery’s Ajax operate continues to be helpful in legacy tasks or situations the place jQuery is already built-in.
Is jQuery’s Ajax Operate Nonetheless Related Immediately?
Sure, however its relevance is dependent upon the undertaking. For legacy programs or tasks already utilizing jQuery, $.ajax() stays a sensible selection. For newer purposes, alternate options like Fetch API, Axios, or SuperAgent are sometimes most well-liked as a consequence of their Promise-based syntax and integration with fashionable frameworks like React and Vue.










