Ever clicked a hyperlink and landed on a “Web page Not Discovered” error? Redirects stop that. They ship guests and search engines like google to the best web page mechanically. Redirects are essential for each website positioning and consumer expertise. For website positioning, they protect hyperlink fairness and maintain your rankings intact. Moreover, it enhances the consumer expertise, as nobody likes useless ends.
Key takeaways
- A redirect mechanically sends customers and search engines like google from one URL to a different, stopping errors like ‘Web page Not Discovered.’
- Redirects are essential for website positioning and consumer expertise, preserving hyperlink fairness and sustaining rankings.
- Several types of redirects exist: 301 for everlasting strikes and 302 for non permanent ones.
- Keep away from client-side redirects, corresponding to meta refresh or JavaScript, as they will hurt website positioning.
- Use Yoast website positioning Premium to simply arrange and handle redirects in your web site.
What’s a redirect?
A redirect is a technique that mechanically sends customers and search engines like google from one URL to a different. For instance, in the event you delete a web page, a redirect can ship guests to a new or associated web page as an alternative of a 404 error.
How redirects work
- A consumer or search engine requests a URL (e.g., yoursite.com/page-old).
- The server responds with a redirect instruction.
- The browser or search engine follows the redirect to the brand new URL (e.g., yoursite.com/page-new).
Redirects can level to any URL, even on a special area.
Why redirects matter
Redirects maintain your web site working easily. With out them, guests hit useless ends, hyperlinks break, and search engines like google get misplaced. They’re not simply technical fixes, as a result of they defend your visitors, protect rankings, and ensure customers land the place they’re speculated to. Whether or not you’re transferring a web page, fixing a typo in a URL, or eradicating previous content material, redirects ensure that nothing will get left behind.
When to make use of a redirect
Use redirects in these situations:
- Deleted pages: Redirect to an identical web page to protect visitors.
- Area adjustments: Redirect the previous area to the brand new one.
- HTTP→HTTPS: Redirect insecure URLs to safe ones.
- URL restructuring: Redirect previous URLs to new ones (e.g., /weblog/submit → /articles/submit).
- Momentary adjustments: Use a 302 for A/B exams or upkeep pages.
Varieties of redirects
There are numerous varieties of redirects, every serving a definite objective. Some are everlasting, some are non permanent, and a few you must keep away from altogether. Right here’s what you should know to select the best one.
Not all redirects work the identical method. A 301 redirect tells search engines like google a web page has moved completely, whereas a 302 redirect alerts a short lived change. Consumer-side redirects, like meta refresh or JavaScript, exist as a result of they’re typically the one choice on restrictive internet hosting platforms or static websites, however they typically create extra issues than they remedy. Beneath, we break down every sort, clarify when to make use of it, and focus on its implications in your website positioning.
Redirect varieties at a look
| Redirect sort | Use case | When to make use of | Browser impression | website positioning impression | website positioning threat |
| 301 | Everlasting transfer | Deleted pages, area adjustments, HTTP→HTTPS | Cached endlessly | Passes (virtually) all hyperlink fairness | None if used appropriately |
| 302 | Momentary transfer | A/B testing, upkeep pages | Not cached | Could not go hyperlink fairness | Can dilute website positioning if used long-term |
| 307 | Momentary transfer (strict) | API calls, non permanent content material shifts | Not cached | Search engines like google might ignore | Excessive if misused |
| 308 | Everlasting transfer (strict) | Uncommon; use 301 as an alternative | Cached endlessly | Passes hyperlink fairness | None |
| Meta Refresh | Consumer-side redirect | Keep away from the place attainable | Gradual, not cached | Unreliable | Excessive (hurts UX/website positioning) |
| JavaScript | Consumer-side redirect | Keep away from the place attainable | Gradual, not cached | Unreliable | Excessive (hurts UX/website positioning) |
301 redirects: Everlasting strikes
A 301 redirect tells browsers and search engines like google {that a} web page has moved completely. Use it when:
- You delete a web page and wish to ship guests to an identical one.
- You modify your area title.
- You turn from HTTP to HTTPS.
website positioning impression: 301 redirects go just about all hyperlink fairness to the brand new URL. However make sure you by no means redirect to irrelevant pages, as this may confuse customers and harm website positioning. For instance, redirecting a deleted weblog submit about “greatest trainers” to your homepage, as an alternative of an identical submit about working gear. This wastes hyperlink fairness and frustrates guests.
Instance HTTP header:
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Completely
Location: https://instance.com/new-page302 redirects: Momentary strikes
A 302 redirect tells browsers and search engines like google {that a} transfer is non permanent. Use it for:
- A/B testing totally different variations of a web page.
- Momentary promotions or gross sales pages.
- Upkeep pages.
website positioning impression: 302 redirects sometimes don’t go rating energy like 301s. Google treats them as non permanent, so they might not protect website positioning worth. For everlasting strikes, at all times use a 301 to make sure hyperlink fairness transfers easily.
Examples of when to make use of a 301 and 302 redirect:
Instance 1: Momentary out-of-stock product (302): A web-based retailer redirects instance.com/red-sneakers to instance.com/blue-sneakers whereas purple sneakers are restocked. A 302 redirect retains the unique URL alive for future use.
Instance 2: A everlasting area change (301): An organization strikes from old-site.com to new-site.com. A 301 redirect makes certain guests and search engines like google land on the brand new area whereas preserving website positioning rankings.
307 and 308 redirects: Strict guidelines
These redirects comply with HTTP guidelines extra strictly than 301 or 302:
- Similar methodology: If a browser sends a POST request, the redirect should additionally use POST.
- Caching:
- 307: By no means cached (non permanent).
- 308: All the time cached (everlasting).
When to make use of them:
- 307: For non permanent redirects the place you should maintain the identical HTTP methodology (e.g., kinds or API calls).
- 308: Nearly by no means, use a 301 as an alternative.
For many websites: Stick to 301 (everlasting) or 302 (non permanent). These are for particular technical circumstances solely.
What to know about client-side redirects:
Consumer-side redirects, corresponding to meta refresh or JavaScript, execute throughout the browser as an alternative of on the server. They’re hardly ever the best selection, however right here’s why you may encounter them:
- Meta refresh: A HTML tag that redirects after a delay (e.g., “You’ll be redirected in 5 seconds…”).
- JavaScript redirects: Code that adjustments the URL after the web page hundreds.
Why must you keep away from them?
- Gradual: The browser should load the web page first, then redirect.
- Unreliable: Search engines like google might ignore them, hurting website positioning.
- Unhealthy UX: Customers see a flash of the unique web page earlier than redirecting.
- Safety dangers: JavaScript redirects might be exploited for phishing.
When they’re used (regardless of the dangers):
- Shared internet hosting with no server entry.
- Legacy techniques or static HTML websites.
- Advert monitoring or A/B testing instruments.
Stick to server-side redirects (301/302) each time attainable. Should you should use a client-side redirect, take a look at it completely and monitor for website positioning points.
How redirects impression website positioning
Redirects do extra than simply ship customers to a brand new URL. They form how search engines like google crawl, index, and rank your web site. A well-planned redirect preserves visitors and rankings. A sloppy one can break each. Right here’s what you should find out about their impression.
Rating energy
301 redirects go a lot of the hyperlink fairness from the previous URL to the brand new one. This helps keep your rankings. 302 redirects might not go rating energy, particularly if used long-term.
Crawl price range
Too many redirects can decelerate how rapidly search engines crawl your web site. Keep away from redirect chains (A→B→C) to save lots of crawl price range.
Person expertise
Redirects stop 404 errors and maintain customers engaged. A clean redirect expertise can cut back bounce charges.
Frequent redirect errors
Redirects appear easy, however small errors could cause large issues. Listed here are the commonest errors and keep away from them.
Redirect chains
A redirect chain occurs when one URL redirects to a different, which redirects to a different, and so forth. For instance:
old-page → new-page → updated-page → final-page
Why it’s dangerous:
- Slows down the consumer expertise.
- Wastes crawl price range, as search engines like google might cease following the chain earlier than reaching the ultimate URL.
- Dilutes rating energy with every hop.
How you can repair it:
- Map previous URLs on to their last vacation spot.
- Use instruments like Screaming Frog to search out and repair chains.
Redirect loops
A redirect loop sends customers and search engines like google in circles. For instance:
page-A → page-B → page-A → page-B...
Why it’s dangerous:
- Customers see an error web page (e.g., “Too many redirects”).
- Search engines like google can’t entry the content material, so it received’t rank.
How you can repair it:
- Verify your redirect guidelines for cblonflicts.
- Check redirects with a software like Redirect Path (Chrome extension) or
curl -vwithin the terminal.
Utilizing 302s for everlasting strikes
A 302 redirect is supposed for non permanent adjustments, however many websites use it for everlasting strikes. For instance:
- Redirecting
old-producttonew-productwith a 302 and leaving it for years.
Why it’s dangerous:
- Search engines like google might not go hyperlink fairness to the brand new URL.
- The previous URL may keep in search outcomes longer than meant.
How you can repair it:
- Use a 301 for everlasting strikes.
- Should you by chance used a 302, swap it to a 301 as quickly as attainable.
Redirecting to irrelevant pages
Redirecting a web page to unrelated content material confuses customers and search engines like google. For instance:
- Redirecting a weblog submit about “greatest trainers” to the homepage or a web page about “kitchen home equipment”.
Why it’s dangerous:
- Customers land on content material they didn’t count on, rising bounce charges.
- Search engines like google might ignore the redirect or penalize it for being manipulative.
- Wastes rating energy that would have been handed to a related web page.
How you can repair it:
- All the time redirect to probably the most related web page accessible.
- If no related web page exists, let the previous URL return a 404 or 410 error as an alternative.
Ignoring inner hyperlinks after redirects
After establishing a redirect, many websites overlook to replace inner hyperlinks. For instance:
- Redirecting
old-pagetonew-pagehowever protecting hyperlinks toold-pagewithin the web site’s navigation or weblog posts.
Why it’s dangerous:
- Inner hyperlinks to the previous URL drive customers and search engines like google by the redirect, slowing down the expertise.
- Wastes crawl price range and dilutes rating energy.
How you can repair it:
- Replace all inner hyperlinks to level on to the brand new URL.
- Use a software like Screaming Frog to search out and repair outdated hyperlinks.
Not testing redirects
Assuming redirects work with out testing can result in surprises. For instance:
- Organising a redirect however not checking if it sends customers to the best place.
- Lacking errors like 404s or redirect loops.
Why it’s dangerous:
- Damaged redirects frustrate customers and harm website positioning.
- Search engines like google might drop pages from the index in the event that they can’t entry them.
How you can repair it:
- Check each redirect manually or with a software.
- Verify Google Search Console for crawl errors after implementing redirects.
Redirecting all the things to the homepage
When a web page is deleted, some websites redirect all visitors to the homepage. For instance:
- Redirecting
old-blog-posttoinstance.comas an alternative of a related weblog submit.
Why it’s dangerous:
- Confuses customers who anticipated particular content material.
- Search engines like google might even see this as a “comfortable 404” and ignore the redirect.
- Wastes rating energy that would have been handed to a related web page.
How you can repair it:
- Redirect to probably the most related web page accessible.
- If no related web page exists, return a 404 or 410 error.
Forgetting to replace sitemaps
After establishing redirects, many websites overlook to replace their XML sitemaps. For instance:
- Maintaining the previous URL within the sitemap whereas redirecting it to a brand new URL.
Why it’s dangerous:
- Sends blended alerts to search engines like google.
- Wastes crawl price range on outdated URLs.
How you can repair it:
- Take away previous URLs from the sitemap.
- Add the brand new URLs to assist search engines like google uncover them quicker.
Utilizing redirects for skinny or duplicate content material
Some websites use redirects to cover skinny or duplicate content material. For instance, redirecting a number of low-quality pages to a single high-quality web page to “clear up” the positioning.
Why it’s dangerous:
- Search engines like google might even see this as manipulative.
- Doesn’t tackle the basis drawback, which is low-quality content material.
How you can repair it:
- Enhance or consolidate content material as an alternative of redirecting.
- Use canonical tags if duplicate content material is unavoidable.
Not monitoring redirects over time
Redirects aren’t a set-it-and-forget-it activity. For instance:
- Organising a redirect and by no means checking if it’s nonetheless wanted or working.
Why it’s dangerous:
- Redirects can break over time (e.g., on account of web site updates or server adjustments).
- Pointless redirects waste crawl price range.
How you can repair it:
- Audit redirects often (e.g., each 6 months).
- Take away redirects which are not wanted.
How you can arrange a redirect
Organising redirects isn’t difficult, however the steps fluctuate relying in your platform. Beneath, you’ll discover simple directions for the commonest setups, whether or not you’re utilizing WordPress, Apache, Nginx, or Cloudflare.
Decide the strategy that matches your setup and comply with alongside. If you’re uncertain which to make use of, begin with the platform you’re most comfy with.
WordPress (utilizing Yoast website positioning Premium)
Yoast website positioning Premium makes it straightforward to arrange redirects, particularly once you delete or transfer content material. Right here’s do it:
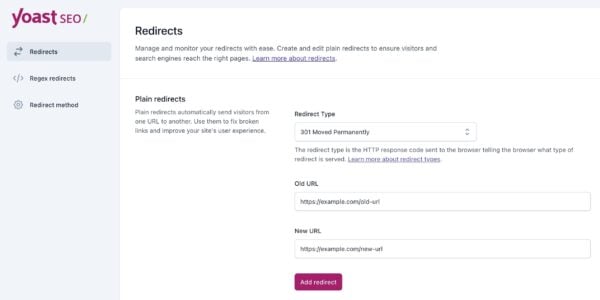
Choice 1: Handbook redirects
- Go to Yoast website positioning → Redirects in your WordPress dashboard.
- Enter the previous URL (the one you wish to redirect from).
- Enter the new URL (the one you wish to redirect to).
- Choose the redirect sort:
- 301 (Everlasting): For deleted or completely moved pages.
- 302 (Discovered): For brief-term adjustments.
- Click on Add Redirect.
Choice 2: Computerized redirects when deleting content material
Yoast website positioning can create redirects mechanically once you delete a submit or web page. Right here’s how:
- Go to Posts or Pages in your WordPress dashboard.
- Discover the submit or web page you wish to delete and click on Trash.
- Yoast website positioning will present a pop-up asking what you’d love to do with the deleted content material. You’ll see two choices:
- Redirect to a different URL: Enter a brand new URL to ship guests to.
- Return a 410 Content material Deleted header: Inform search engines like google that the web page is completely deleted and ought to be faraway from their index.
- Choose your most popular choice and make sure.
This characteristic saves time and ensures guests land on the best web page. No guide setup required.
Need assistance with redirects? Strive Yoast website positioning Premium
No code, no problem. Simply smarter redirects and lots of different invaluable instruments.
Apache (.htaccess file)
Apache makes use of the .htaccess file to handle redirects. In case your web site runs on Apache, that is the best solution to set them up. Add the foundations under to your .htaccess file, guaranteeing it is situated in the basis listing of your web site.
Add these strains to your .htaccess file:
# 301 Redirect
Redirect 301 /old-page.html /new-page.html# 302 Redirect
Redirect 302 /temporary-page.html /new-page.htmlNginx (server config)
Nginx handles redirects within the server configuration file. In case your web site runs on Nginx, add these guidelines to your server block after which reload the service to use the adjustments.
Add this to your server configuration:
# 301 Redirect
server {
pay attention 80;
server_name instance.com;
return 301 https://instance.com$request_uri;
}# 302 Redirect
server {
pay attention 80;
server_name instance.com;
location = /old-page {
return 302 /new-page;
}
}Cloudflare (web page guidelines)
Cloudflare means that you can arrange redirects with out modifying server recordsdata. Create a web page rule to ahead visitors from one URL to a different, with out requiring any coding. Merely enter the previous and new URLs, choose the redirect sort, and click on Save.
- Go to Guidelines → Web page Guidelines.
- Enter the previous URL (e.g., instance.com/old-page).
- Choose Forwarding URL and select 301 or 302.
- Enter the brand new URL (e.g., https://instance.com/new-page).
Troubleshooting redirects
Redirects don’t at all times work as anticipated. A typo, a cached web page, or a conflicting rule can break them, or worse, create loops that frustrate customers and search engines like google. Beneath are the commonest points and repair them.
If one thing’s not working, begin with the fundamentals: examine for errors, take a look at completely, and clear your cache. The options are normally less complicated than they appear.
Why isn’t my redirect working?
- Verify for typos: Make sure the URLs are appropriate.
- Clear your cache: Browsers cache 301 redirects aggressively.
- Check with curl: Run
curl -v http://yoursite.com/old-urlto see the HTTP headers.
Can redirects harm website positioning?
Sure, in the event you:
- Create redirect chains (
A→B→C) - Use 302s for everlasting strikes
- Redirect to irrelevant pages
How do I discover damaged redirects?
- Use Google Search Console → Protection report.
- Use Screaming Frog to crawl your web site for 404s and redirects.
What’s the distinction between a 301 and 308 redirect?
- 301: Commonest for everlasting strikes. Broad browser help.
- 308: Strict everlasting redirect. Hardly ever used. Similar website positioning impression as 301.
What’s a proxy redirect?
A proxy redirect retains the URL the identical within the browser however fetches content material from a special location. Used for load balancing or A/B testing. Keep away from for website positioning, as search engines like google might not comply with them.
Conclusion about redirects
Redirects are a easy however highly effective software. A redirect mechanically sends customers and search engines like google from one URL to a different. In consequence, they maintain your web site working easily and protect website positioning worth and rating energy. Bear in mind:
- Use 301 redirects for everlasting strikes.
- Use 302 redirects for non permanent adjustments.
- Keep away from client-side redirects, corresponding to meta refresh or JavaScript.
Need assistance? Strive Yoast website positioning Premium’s redirect supervisor.